Ameliorative Effects of Rhoifolin in Scopolamine-Induced Amnesic Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model
- PMID: 32635149
- PMCID: PMC7401873
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9070580
Ameliorative Effects of Rhoifolin in Scopolamine-Induced Amnesic Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model
Abstract
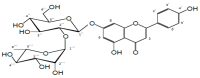
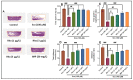
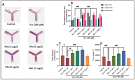
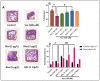
Rhoifolin (Rho) exerts many biological activities such as anticancer, antidiabetic, hepatoprotective, antirheumatic, antibacterial, and antiviral properties. The neuroprotective action of this compound has not been studied. The goal of this study was to investigate the improvement impact of Rho on scopolamine (Sco)-induced zebrafish anxiety, amnesia, and brain oxidative stress and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms involved. Zebrafish were treated with Rho (1, 3, and 5 μg/L) for nine consecutive days and were subsequently subjected to Sco (100 μM) 30 min before behavioral tests (novel tank diving test, Y-maze, and novel object recognition tests). Rho was isolated from Chorisia crispiflora (Malvaceae) leaves and identified by different spectroscopic techniques. To further assess the possible mechanisms of Rho in enhancing the memory capacities in zebrafish, the in vivo antioxidant status and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity was also evaluated. Rho from Chorisia crispiflora leaves was identified. Rho could alleviate anxiety, memory deficits, and brain oxidative stress in Sco-treated zebrafish and could regulate the cholinergic function by inhibiting the AChE activity. Our results demonstrated that Rho could be a promising candidate compound against anxiety and amnesia by restoring the cholinergic activity and the amelioration of brain oxidative stress.
Keywords: anxiety; cholinergic function; memory; oxidative stress; rhoifolin; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Liu W., Zhu Y., Wang Y., Qi S., Wang Y., Ma C., Li S., Jiang B., Cheng X., Wang Z., et al. Anti-amnesic effect of extract and alkaloid fraction from aerial parts of Peganum harmala on scopolamine-induced memory deficits in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017;204:95–106. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.04.019. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

