Analysis of the Imaging Characteristics of Holographic Waveguides Recorded in Photopolymers
- PMID: 32635228
- PMCID: PMC7408443
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12071485
Analysis of the Imaging Characteristics of Holographic Waveguides Recorded in Photopolymers
Abstract
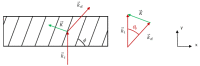
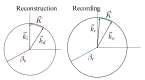
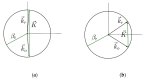
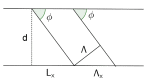
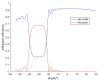
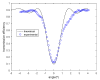
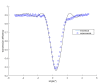
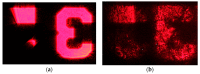
In this work, we study the imaging characteristics of an optical see-through display based on a holographic waveguide. To fabricate this device, two transmission holograms are recorded on a photopolymer material attached to a glass substrate. The role of the holograms is to couple the incident light between air and the glass substrate, accomplishing total internal reflection. The role of noise reflection gratings and shrinkage on the imaging characteristics of the device will be also explored. The holograms (slanted transmission gratings with a spatial frequency of 1690 lines/mm) were recorded on a polyvinyl alcohol acrylamide holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystal (HPDLC) material. We will show that sufficient refractive index modulation is achieved in the material, in order to obtain high diffraction efficiencies. We will demonstrate that the final device acts as an image formation system.
Keywords: diffraction gratings; holographic waveguide; holography; photopolymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Khrapko R., Lai C., Casey J., Wood W.A., Borrelli N.F. Accumulated self-focusing of ultraviolet light in silica glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014;105:244110. doi: 10.1063/1.4904098. - DOI
-
- Cameron A. The application of holographic optical waveguide technology to q-sight family of helmet-mounted displays; Proceedings of the SPIE Optics + Photonics 2009; San Diego, CA, USA. 2–6 August 2009; p. 73260H.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

