Marine Excitatory Amino Acids: Structure, Properties, Biosynthesis and Recent Approaches to Their Syntheses
- PMID: 32635311
- PMCID: PMC7412112
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25133049
Marine Excitatory Amino Acids: Structure, Properties, Biosynthesis and Recent Approaches to Their Syntheses
Abstract
This review considers the results of recent studies on marine excitatory amino acids, including kainic acid, domoic acid, dysiherbaine, and neodysiherbaine A, known as potent agonists of one of subtypes of glutamate receptors, the so-called kainate receptors. Novel information, particularly concerning biosynthesis, environmental roles, biological action, and syntheses of these marine metabolites, obtained mainly in last 10-15 years, is summarized. The goal of the review was not only to discuss recently obtained data, but also to provide a brief introduction to the field of marine excitatory amino acid research.
Keywords: domoic acid; dysiherbaine; kainic acid; neodysiherbaine A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



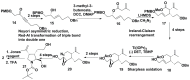

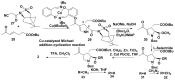

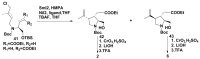








References
-
- Shimizu Y., Gupta S., Masuda K., Moranda L., Walker C.R., Wang R. Dinoflagellate and other microalgal toxins; chemistry and biochemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1989;61:513–516. doi: 10.1351/pac198961030513. - DOI
-
- Stonik V.A., Stonik I.V. Toxins produced by marine microorganisms: A short review. In: Gopalakrishnakone P., Haddad J.V., Tubaro A., Kim E., Kem W., editors. Marine and Freshwater Toxins. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2016. pp. 3–21. - DOI
-
- Stonik I.V., Orlova T.Y. Domoic acid-producing diatoms of the genus Pseudo-nitzschia H. Peragallo, 1900 (Bacillariophyta) from the North Pacific. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2018;44:347–354. doi: 10.1134/S1063074018050127. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

