Combination Antioxidant/NSAID Therapies and Oral/Topical Ocular Delivery Modes for Prevention of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in a Rat Model
- PMID: 32635350
- PMCID: PMC7400869
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12071980
Combination Antioxidant/NSAID Therapies and Oral/Topical Ocular Delivery Modes for Prevention of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in a Rat Model
Abstract
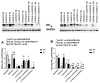
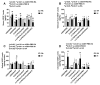
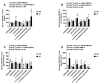
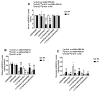
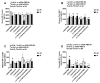
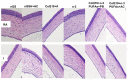
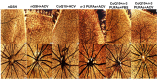
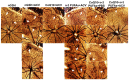
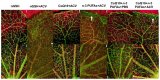
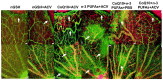
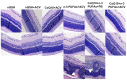
Given the complexity of oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR), we tested the hypothesis that combination therapies and modes of administration would synergistically optimize efficacy for prevention of OIR. Newborn rats were exposed to neonatal intermittent hypoxia (IH) from the first day of life (P0) until P14 during which they received: (1) oral glutathione nanoparticles (nGSH) with topical ocular phosphate buffered saline (PBS); (2) nGSH with topical ocular Acuvail (ACV); (3) oral coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) + ACV; (4) oral omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFAs) + ACV; (5) CoQ10 + n-3 PUFAs + PBS; or (6) CoQ10 + n-3 PUFAs + ACV. Treated groups raised in room air (RA) served as controls. At P14, pups were placed in RA with no treatment until P21. Retinal vascular pathology, ocular angiogenesis biomarkers, histopathology, and morphometry were determined. All combination treatments in IH resulted in the most beneficial retinal outcomes consistent with suppression of angiogenesis growth factors during reoxygenation/reperfusion and no significant adverse effects on somatic growth. nGSH + PBS also reversed IH-induced retinopathy, but had negative effects on growth. Simultaneously targeting oxidants, inflammation, and poor growth mitigates the damaging effects of neonatal IH on the developing retina. Therapeutic synergy with combination delivery methods enhance individual attributes and simultaneously target multiple pathways involved in complex diseases such as OIR.
Keywords: coenzyme Q10; glutathione nanoparticles; insulin-like Growth Factor-I; ketorolac; n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids; neonatal intermittent hypoxia; oxygen-induced retinopathy; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomarkers of lung alveolarization and microvascular maturation in response to intermittent hypoxia and/or early antioxidant/fish oil supplementation in neonatal rats.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2023 Aug;58(8):2352-2363. doi: 10.1002/ppul.26495. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2023. PMID: 37265429 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, antioxidants, and/or non-steroidal inflammatory drugs in the brain of neonatal rats exposed to intermittent hypoxia.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2021 Aug;81(5):448-460. doi: 10.1002/jdn.10120. Epub 2021 May 25. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33969544
-
Comparative Effects of Coenzyme Q10 or n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Retinal Angiogenesis in a Rat Model of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Nov 9;7(11):160. doi: 10.3390/antiox7110160. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30423931 Free PMC article.
-
[Pathological role of apelin in angiogenic eye disease].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2011;131(8):1201-6. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.131.1201. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2011. PMID: 21804324 Review. Japanese.
-
The Role of Citicoline and Coenzyme Q10 in Retinal Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 7;24(6):5072. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065072. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982157 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of coenzyme Q10 or fish oil for prevention of intermittent hypoxia-induced oxidative injury in neonatal rat lungs.Respir Res. 2021 Jul 5;22(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01786-w. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 34225702 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of lung alveolarization and microvascular maturation in response to intermittent hypoxia and/or early antioxidant/fish oil supplementation in neonatal rats.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2023 Aug;58(8):2352-2363. doi: 10.1002/ppul.26495. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2023. PMID: 37265429 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Glutathione Nanoparticles, CoEnzyme Q10, and Fish Oil for Prevention of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in Neonatal Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Mar 17;17(3):381. doi: 10.3390/ph17030381. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Phelps D.L. Retinopathy of prematurity: History, classification, and pathophysiology. Neoreviews. 2001;2:e153–e166. doi: 10.1542/neo.2-7-e153. - DOI
-
- Phelps D.L. Retinopathy of prematurity. In: Fanaroff A.A., Martin R.J., editors. Neonatal Perinatal Medicine: Diseases of the Fetus and Infant. 7th ed. Volume 2. Mosby; St. Louis, MO, USA: 2002. pp. 1595–1599.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

