The Relationships between Physical Activity and Life Satisfaction and Happiness among Young, Middle-Aged, and Older Adults
- PMID: 32635457
- PMCID: PMC7369812
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17134817
The Relationships between Physical Activity and Life Satisfaction and Happiness among Young, Middle-Aged, and Older Adults
Abstract
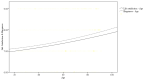
Physical activity has benefits on physical and psychological health. The aims of this study were to investigate (1) the relationships between physical activity and life satisfaction and happiness in young, middle-aged, and older adults while controlling for demographic characteristics, and (2) the relationships between age and life satisfaction and happiness for different physical activity levels. A total of 2345 healthy adults were recruited. Demographic characteristic, physical activity, life satisfaction, and happiness were collected. Participants were divided into young, middle-aged, and older adult groups based on age, and physical activity was categorized as high, moderate, and low. After controlling for demographic characteristics, participants with high and moderate activity levels had significantly higher life satisfaction and happiness than those with a low activity level across the total population and the three age groups. Age squared was a significant predictor of a positive curvilinear between age and life satisfaction and happiness. Physical activity was significantly related to life satisfaction and happiness in young, middle-aged, and older adults. In addition, life satisfaction and happiness increased with increasing age. The results support the promotion of physical activity.
Keywords: exercise; happiness; life satisfaction; life span; physical activity subjective well-being.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Diener E., Suh E.M., Lucas R.E., Smith H.L. Subjective well-being: Three decades of progress. Psychol. Bull. 1999;125:276–302. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.125.2.276. - DOI
-
- Pavot W., Diener E. Review of the satisfaction with life scale. In: Diener E., editor. Assessing Well-Being. Social Indicators Research Series. Volume 39. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2009. pp. 101–117.
-
- Shin D.C., Johnson D.M. Avowed happiness as an overall assessment of the quality of life. Soc. Indic. Res. 1978;5:475–492. doi: 10.1007/BF00352944. - DOI
-
- Veenhoven R. Happiness: Also known as “life satisfaction” and “subjective well-being”. In: Land K.C., Michalos A.C., Sirgy M.J., editors. Handbook of Social Indicators and Quality of Life Research. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2012. pp. 63–77.
-
- Magen Z. Commitment beyond self and adolescence: The issue of happiness. Soc. Indic. Res. 1996;37:235–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00286233. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical