JAK-Inhibitors for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Focus on the Present and an Outlook on the Future
- PMID: 32635659
- PMCID: PMC7408575
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10071002
JAK-Inhibitors for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Focus on the Present and an Outlook on the Future
Abstract
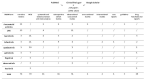
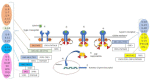
Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) belong to a new class of oral targeted disease-modifying drugs which have recently revolutionized the therapeutic panorama of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other immune-mediated diseases, placing alongside or even replacing conventional and biological drugs. JAKi are characterized by a novel mechanism of action, consisting of the intracellular interruption of the JAK-STAT pathway crucially involved in the immune response. The aim of this narrative review is to globally report the most relevant pharmacological features and clinical outcomes of the developed and incoming JAKi for RA, based on the available preclinical and clinical evidence. A total of 219 papers, including narrative and systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials (RCTs), observational studies, case reports, guidelines, and drug factsheets, were selected. The efficacy and safety profile of both the first generation JAKi (baricitinib and tofacitinib) and the second generation JAKi (upadacitinib, filgotinib, peficitinib, decernotinib and itacitinib) were compared and discussed. Results from RCTs and real-life data are encouraging and outline a rapid onset of the pharmacologic effects, which are maintained during the time. Their efficacy and safety profile are comparable or superior to those of biologic agents and JAKi proved to be efficacious when given as monotherapy. Finally, the manufacturing of JAKi is relatively easier and cheaper than that of biologics, thus increasing the number of compounds being formulated and tested for clinical use.
Keywords: Janus kinase-inhibitors; Janus kinases; rheumatoid arthritis; small molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

