Interferon-independent STING signaling promotes resistance to HSV-1 in vivo
- PMID: 32636381
- PMCID: PMC7341812
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-17156-x
Interferon-independent STING signaling promotes resistance to HSV-1 in vivo
Abstract
The Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) pathway initiates potent immune responses upon recognition of DNA. To initiate signaling, serine 365 (S365) in the C-terminal tail (CTT) of STING is phosphorylated, leading to induction of type I interferons (IFNs). Additionally, evolutionary conserved responses such as autophagy also occur downstream of STING, but their relative importance during in vivo infections remains unclear. Here we report that mice harboring a serine 365-to-alanine (S365A) mutation in STING are unexpectedly resistant to Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)-1, despite lacking STING-induced type I IFN responses. By contrast, resistance to HSV-1 is abolished in mice lacking the STING CTT, suggesting that the STING CTT initiates protective responses against HSV-1, independently of type I IFNs. Interestingly, we find that STING-induced autophagy is a CTT- and TBK1-dependent but IRF3-independent process that is conserved in the STING S365A mice. Thus, interferon-independent functions of STING mediate STING-dependent antiviral responses in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
R.E.V. has a financial relationship with Aduro BioTech and Ventus Therapeutics, and both he and the companies may benefit from the commercialization of the results of this research. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
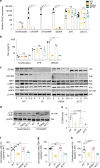
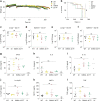
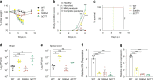

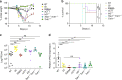
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

