Pyrophen Isolated from the Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus Strain KARSV04 Synergizes the Effect of Doxorubicin in Killing MCF7 but not T47D Cells
- PMID: 32636705
- PMCID: PMC7336043
- DOI: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2019.30633
Pyrophen Isolated from the Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus Strain KARSV04 Synergizes the Effect of Doxorubicin in Killing MCF7 but not T47D Cells
Abstract
Objectives: Pyrophen, an amino acid-pyrone derivative isolated from Aspergillus fumigatus strain KARSV04 has been reported to have an anticancer effect on T47D cells by inhibiting the growth of cells and modulating the cell cycle in the S phase. In the present study, the effect of pyrophen in doxorubicin (Dox) chemotherapy in an in vitro model of breast cancers was studied.
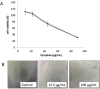
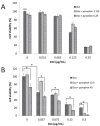
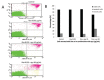
Materials and methods: The cytotoxicity of pyrophen and Dox separately and in combination were evaluated in T47D and MCF-7 cells by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. Modulation of cell cycle distribution and apoptosis was examined by flow cytometry.
Results: Our findings showed that pyrophen did not significantly potentiate Dox-induced cytotoxicity in T47D cells. Adding Dox-treated T47D cells with pyrophen at a concentration of 9.20 μg/mL induced a slight increase in the S-phase cell population. This compound induced cytotoxicity of MCF-7 cells with IC50 of 70.57 μg/mL. Co-treatment of pyrophen and Dox in MCF-7 cells increased cytotoxicity relative to Dox alone, which was suggested in part to be due to modulation of the cell cycle in the G2/M phase and apoptosis.
Conclusion: The data suggest different mechanisms of regulation in promoting cell death by two different cell lines in response to administration of pyrophen.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; MCF-7; T47D; doxorubicin; pyrophen.
©Copyright 2020 Turk J Pharm Sci, Published by Galenos Publishing House.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:359–386. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Moretti E, Oakman C, Di Leo A. Predicting anthra-cycline benefit: have we made any progress? Curr Opin Oncol. 2009;21:507–515. - PubMed
-
- Roca-Alonso L, Pellegrino L, Castellano L, Stebbing J. Breast cancer treatment and adverse cardiac events: what are the molecular mechanisms? Cardiology. 2012;122:253–259. - PubMed
-
- Kugawa F, Ueno A. Profiles of caspase activation and gene expression in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7, after cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, 5-fluorouracil (CDF) multi-drug administration. J Health Sci. 2010;56:81–87.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
