This is a preprint.
High affinity binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein enhances ACE2 carboxypeptidase activity
- PMID: 32637947
- PMCID: PMC7337377
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.07.01.182659
High affinity binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein enhances ACE2 carboxypeptidase activity
Update in
-
High affinity binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein enhances ACE2 carboxypeptidase activity.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 25;295(52):18579-18588. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015303. Epub 2020 Oct 29. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33122196 Free PMC article.
Abstract
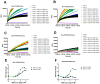
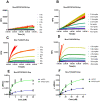
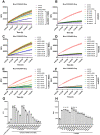
A novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) has emerged to a global pandemic and caused significant damages to public health. Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2(ACE2) was identified as the entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2. As a carboxypeptidase, ACE2 cleaves many biological substrates besides Ang II to control vasodilatation and permeability. Given the nanomolar high affinity between ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, we wonder how this interaction would affect the enzymatic activity of ACE2. Surprisingly, SARS-CoV-2 trimeric spike protein increased ACE2 proteolytic activity ~3-10 fold when fluorogenic caspase-1 substrate and Bradykinin-analog peptides were used to characterize ACE2 activity. In addition, the enhancement was mediated by ACE2 binding of RBD domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike. These results highlighted the altered activity of ACE2 during SARS-CoV-2 infection and would shed new lights on the pathogenesis of COVID-19 and its complications for better treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures

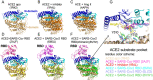
References
-
- Wichmann D. et al. Autopsy Findings and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients With COVID-19. Ann Intern Med (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
