Interferon-Independent Activities of Mammalian STING Mediate Antiviral Response and Tumor Immune Evasion
- PMID: 32640258
- PMCID: PMC7365768
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.009
Interferon-Independent Activities of Mammalian STING Mediate Antiviral Response and Tumor Immune Evasion
Abstract
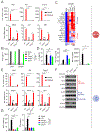
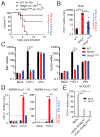
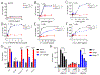
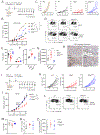
Type I interferon (IFN) response is commonly recognized as the main signaling activity of STING. Here, we generate the Sting1S365A/S365A mutant mouse that precisely ablates IFN-dependent activities while preserving IFN-independent activities of STING. StingS365A/S365A mice protect against HSV-1 infection, despite lacking the STING-mediated IFN response. This challenges the prevailing view and suggests that STING controls HSV-1 infection through IFN-independent activities. Transcriptomic analysis reveals widespread IFN-independent activities of STING in macrophages and T cells, and STING activities in T cells are predominantly IFN independent. In mouse tumor models, T cells in the tumor experience substantial cell death that is in part mediated by IFN-independent activities of STING. We found that the tumor induces STING-mediated cell death in T cells to evade immune control. Our data demonstrate that mammalian STING possesses widespread IFN-independent activities that are important for restricting HSV-1 infection, tumor immune evasion and likely also adaptive immunity.
Keywords: HSV-1; IFN; STING; T cells; antiviral response; cancer immunology.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
IFN-Independent STING Signaling: Friend or Foe?Immunity. 2020 Jul 14;53(1):8-10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.021. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32668231
References
-
- Bouis D, Kirstetter P, Arbogast F, Lamon D, Delgado V, Jung S, Ebel C, Jacobs H, Knapp A-M, Jeremiah N, et al. (2018). Severe combined immunodeficiency in Sting V154M/WT mice. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. - PubMed
-
- Cerboni S, Jeremiah N, Gentili M, Gehrmann U, Conrad C, Stolzenberg M-C, Picard C, Neven B, Fischer A, Amigorena S, et al. (2017). Intrinsic antiproliferative activity of the innate sensor STING in T lymphocytesSTING inhibits T cell proliferation. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 214, jem.20161674. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

