Potential treatment strategy for the rare osimertinib resistant mutation EGFR L718Q
- PMID: 32642185
- PMCID: PMC7330377
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2020.03.29
Potential treatment strategy for the rare osimertinib resistant mutation EGFR L718Q
Abstract
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) L718Q is a rare resistant mutation which independently leads to third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) resistance. Although a few studies have examined its resistance mechanisms, no effective treatment strategy has yet been proposed for patients with this mutation. Here, we report an effective treatment strategy for the rare EGFR L718Q mutation for the first time. A 44-year-old Chinese male patient initially presented with the sensitizing EGFR L858R mutation, and the progression-free survival (PFS) time after initial icotinib treatment was 9 months. When the progression of the disease (PD) and the EGFR T790M mutation were identified, he did not respond to the osimertinib treatment. Through comprehensive next-generation sequencing (NGS) of the surgical specimen, the rare EGFR L718Q mutation was eventually identified as having a frequency of 68.84%, together with an EGFR amplification with a copy number of 11.54. The previous treatment response was retrospectively explained, and the patient faced the challenge of not being able to benefit from any targeted therapy. Following chemotherapy with a personalized regimen which effectively modified the proportion of sensitive and resistant cells, significant response to osimertinib re-challenge was observed, and another PFS of 4.7 months was achieved. Unfortunately, four EGFR mutations, EGFR L858, T790M, L718Q, and C797S, were simultaneously detected in his late stage, and led to further progression of disease.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) L718Q; osimertinib resistance; treatment strategy; tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) re-challenge.
2020 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2020.03.29). SZ reports grants from National Key Research and Development Program of China Grant, during the conduct of the study. NL reports grants from Beijing Natural Science Foundation, grants from Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, grants from Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Young Medical Talent Award Fund, grants from Beijing Students’ platform for innovation and entrepreneurship training program, during the conduct of the study. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
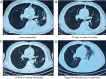
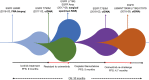
Comment in
-
Treatment strategy of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Mar;14(3):602-606. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-177. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35399242 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Potential treatment strategy for the rare osimertinib resistant EGFR L718Q mutation.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Mar;14(3):599-601. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-100. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35399244 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Future prospects of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) and surgery for non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Apr;14(4):809-811. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-57. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35572861 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Multidisciplinary and real life data: practical management of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).J Thorac Dis. 2022 Apr;14(4):805-808. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-181. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35572878 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Tracking and tackling the tumor dynamics clonal evolution: osimertinib rechallenge after interval therapy might be an effective treatment approach in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).J Thorac Dis. 2022 Apr;14(4):816-819. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-98. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35572898 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Intratumoral and intertumoral heterogeneity drives EGFR treatment considerations.J Thorac Dis. 2022 May;14(5):1299-1301. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-312. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35693600 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Critical points in the management of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Jun;14(6):1748-1752. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-269. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35813737 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: current advances and challenges.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Jun;14(6):1753-1757. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-364. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35813756 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The emerging landscape of EFGR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung adenocarcinoma-successes and challenges.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Jun;14(6):1766-1771. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-432. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35813761 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
