Transthoracic versus intra-operative transesophageal echocardiography in right heart assessment
- PMID: 32642208
- PMCID: PMC7330327
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2020.02.04
Transthoracic versus intra-operative transesophageal echocardiography in right heart assessment
Abstract
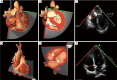
Methods: Fifty-four patients who had combined mitral and tricuspid valve surgery were included. Right heart measurements were performed in the TTE apical 4-chamber (A4C) and RV inflow views, and TEE mid-esophageal 4-chamber (ME4C) and transgastric RV inflow views at end-diastole. Spearman correlation coefficients (r) were applied to test for associations between the imaging modalities.
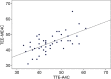
Results: The mean age was 65 years and 39% were male. All patients had ≥ moderate tricuspid regurgitation (TR), and a secondary/functional etiology was present in 89%. The median TAd and RV basal (RVd) diameters in the TTE-A4C view measured 37 mm [interquartile range (IQR), 34-44] and 43 mm (IQR, 40-51), respectively. The TTE-A4C TAd strongly correlated with the TEE-ME4C measurement (r=0.72), with an overestimation of 1 mm (IQR, -2 to 4) by TEE (P<0.01). For RVd, the TTE-A4C measurement correlated moderately with the TEE-ME4C view (r=0.61), underestimating the RVd by -1 mm (IQR, -4 to 3.3) (P<0.01). No correlation was observed between TAPSE measured by TTE and TEE (r=0.22, P=0.13).
Conclusions: Intra-operative TEE may reliably quantitate TA and RV size and geometry. The current findings are best interpreted as hypothesis-generating for future validative studies.
Keywords: Intra-operative transesophageal echocardiography (TEE); right ventricle; tricuspid valve; two-dimensional echocardiography.
2020 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2020.02.04). The series “Novel Concepts in Cardiopulmonary and Structural Heart Disease” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. CGM served as the unpaid Guest Editor of the series and serves as an unpaid editorial member of Journal of Thoracic Disease from Jan 2019 to Dec 2020. FN serves as an unpaid editorial member of Journal of Thoracic Disease from Aug 2019 to Jul 2021. The other authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Hung J, Koelling T, Semigran MJ, et al. Usefulness of echocardiographic determined tricuspid regurgitation in predicting event-free survival in severe heart failure secondary to idiopathic-dilated cardiomyopathy or to ischemic cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol 1998;82:1301-3. 10.1016/S0002-9149(98)00624-9 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
