Excess all-cause mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic in Europe - preliminary pooled estimates from the EuroMOMO network, March to April 2020
- PMID: 32643601
- PMCID: PMC7346364
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.26.2001214
Excess all-cause mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic in Europe - preliminary pooled estimates from the EuroMOMO network, March to April 2020
Abstract
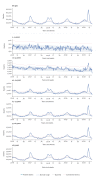
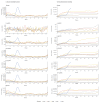
A remarkable excess mortality has coincided with the COVID-19 pandemic in Europe. We present preliminary pooled estimates of all-cause mortality for 24 European countries/federal states participating in the European monitoring of excess mortality for public health action (EuroMOMO) network, for the period March-April 2020. Excess mortality particularly affected ≥ 65 year olds (91% of all excess deaths), but also 45-64 (8%) and 15-44 year olds (1%). No excess mortality was observed in 0-14 year olds.
Keywords: All-cause mortality; Covid-19 pandemic; EuroMOMO; Europe.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Situation Report 1. Geneva: WHO; 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2...
-
- WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. World Health Organization: Geneva; 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re...
-
- Bernard Stoecklin S, Rolland P, Silue Y, Mailles A, Campese C, Simondon A, et al. Investigation Team First cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in France: surveillance, investigations and control measures, January 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020;25(6):2000094. 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.6.2000094 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
