Computer-based cognitive interventions in acquired brain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 32645046
- PMCID: PMC7347178
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235510
Computer-based cognitive interventions in acquired brain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Introduction: Acquired brain injury (ABI) leads to cognitive deficits in a great variety of cognitive functions. Interventions aimed at reducing such deficits include the use of computer-based cognitive interventions. The present work synthetizes and quantitively analyses the effect of computer-based cognitive interventions in ABI.
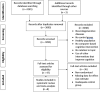
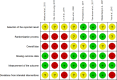
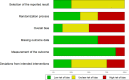
Methods: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, ProQuest and Ovid databases were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCT) addressing this issue. A total number of 8 randomized-controlled trials were included for systematic review and meta-analysis. Univariate meta-analyses were conducted for every cognitive function, producing aggregates when a study contributed more than one effect size per cognitive domain.
Results: Random-effects meta-analyses showed an improvement of Visual and Verbal working memory, while other domains like Attention, Processing speed, Executive functions and Memory were not benefited by the interventions.
Conclusions: Computer-based cognitive interventions might be a beneficial intervention for ABI population to improve Visual and Verbal working memory, although no effect was found in other cognitive domains. Implications and possible future directions of the research are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Dikmen SS, Machamer JE, Powell JM, Temkin NR. Outcome 3 to 5 Years After Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. 2003;84:9. - PubMed
-
- Park YH, Jang J-W, Park SY, Wang MJ, Lim J-S, Baek MJ, et al. Executive Function as a Strong Predictor of Recovery from Disability in Patients with Acute Stroke: A Preliminary Study. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases. 2015;24(3):554–61. 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.09.033 - DOI - PubMed

