Patterns of Antiretroviral Therapy Use and Immunologic Profiles at Enrollment in the REPRIEVE Trial
- PMID: 32645162
- PMCID: PMC7347081
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa259
Patterns of Antiretroviral Therapy Use and Immunologic Profiles at Enrollment in the REPRIEVE Trial
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Patterns of Antiretroviral Therapy Use and Immunologic Profiles at Enrollment in the REPRIEVE Trial.J Infect Dis. 2021 Feb 3;223(2):352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa594. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33068427 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Patterns of antiretroviral therapy (ART) use and immunologic correlates vary globally, and contemporary trends are not well described.
Methods: The REPRIEVE trial (Randomized Trial to Prevent Vascular Events in HIV) enrolled persons with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) who were aged 40-75 years, receiving ART, and had low-to-moderate cardiovascular disease risk. ART use was summarized within Global Burden of Disease (GBD) super-regions, with adjusted linear and logistic regression analyses examining associations with immune parameters and key demographics.
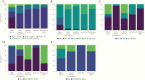
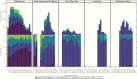
Results: A total of 7770 participants were enrolled, with a median age of 50 years (interquartile range, 45-55 years); 31% were female, 43% were black or African American, 15% were Asian, 56% had a body mass index >25 (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared), and 49% were current or former smokers. The median CD4 T-cell count was 620/µL (interquartile range, 447-826/ µ L), and the median duration of prior ART use, 9.5 years (5.3-14.8) years. The most common ART regimens were nucleoside/nucleotide reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) plus nonnucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (43%), NRTI plus integrase strand transfer inhibitor (25%), and NRTI plus protease inhibitor (19%). Entry ART varied by GBD region, with shifts during the trial enrollment period. In adjusted analyses, entry CD4 cell count and CD4/CD8 ratio were associated with GBD region, sex, entry regimen, duration of ART, and nadir CD4 cell count; CD4 and CD8 cell counts were also associated with body mass index and smoking status.
Conclusions: There were substantial variations in ART use by geographic region and over time, likely reflecting the local availability of specific medications, changes in treatment guidelines and provider/patient preferences. The analyses of CD4 cell counts and CD4/CD8 ratios may provide valuable insights regarding immune correlates and outcomes in people living with HIV.
Clinical trials registration: NCT02344290.
Keywords: CD4 cell count; CD4/CD8 ratio; HIV; REPRIEVE; antiretroviral therapy; cardiovascular disease; pitavastatin calcium; statins.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS (UNAIDS). Fact sheet—latest statistics on the status of the AIDS epidemic: UNAIDS. 2017. http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet. Accessed 4 January 2020.
-
- Danforth K, Granich R, Wiedeman D, Baxi S, Padian N. Global mortality and morbidity of HIV/AIDS. In: Holmes KK, Bertozzi S, Bloom BR, Jha P, eds. Major infectious diseases. Washington, DC: The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS (UNAIDS). Ending AIDS: progress towards the 90-90-90 targets. Global AIDS update 2019 https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2019/2019-UNAIDS-data. Accessed 29 January 2020.
-
- Hoffmann U, Lu MT, Olalere D, et al. ; REPRIEVE Investigators Rationale and design of the mechanistic substudy of the Randomized Trial to Prevent Vascular Events in HIV (REPRIEVE): effects of pitavastatin on coronary artery disease and inflammatory biomarkers. Am Heart J 2019; 212:1–12. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK040561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069463/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069399/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123339/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069463/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002384/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069521/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123336/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI106701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States

