A Nano Drug Delivery System Based on Angelica sinensis Polysaccharide for Combination of Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy
- PMID: 32646040
- PMCID: PMC7411593
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25133096
A Nano Drug Delivery System Based on Angelica sinensis Polysaccharide for Combination of Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy
Abstract
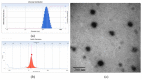
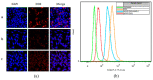
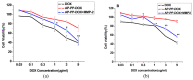
Combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy has been a promising strategy in cancer treatment. Polysaccharides from Angelica sinensis (AP), a well-known Chinese herbal medicine, have been proved to have good immunomodulatory activity. In the present study, an enzyme-sensitive tumor-targeting nano drug delivery system (AP-PP-DOX (doxorubicin), PP stood for peptide) was constructed. In this system, Angelica polysaccharides act as not only carriers to targeted delivery of drugs to tumor tissue but also effectors to improve tumor microenvironment and enhance immune function, resulting in synergistic antitumor effect with chemotherapy drugs. The structure of this conjugate was confirmed by FI-IR and 1H-NMR. The particle size and zeta potential of the nanoparticles were 129.00 ± 3.32 nm and -28.45 ± 0.22 mV, respectively. Doxorubicin (DOX) and AP could be quickly released from the AP-PP-DOX under the presence of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2). The released DOX showed good antitumor efficacy in vitro. The treatment of released AP moiety increased the expression of IL-2, while that of IL-10 was decreased, showing potential in restoring Th1/Th2 immune balance in tumor microenvironment. In a word, this drug delivery system, with specific tissue targeting and tumor microenvironment improvement, will open a new avenue for combination treatment of cancer.
Keywords: Angelica sinensis polysaccharide; doxorubicin; enzymes sensitive drug delivery; synergistic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Cao W., Li X.Q., Wang X., Fan H.T., Zhang X.N., Hou Y., Liu S.B., Mei Q.B. A novel polysaccharide, isolated from Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels induces the apoptosis of cervical cancer HeLa cells through an intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Phytomedicine. 2010;17:598–605. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2009.12.014. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

