Efficient implied alignment
- PMID: 32646365
- PMCID: PMC7350648
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-020-03595-2
Efficient implied alignment
Abstract
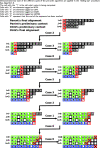
Background: Given a binary tree [Formula: see text] of n leaves, each leaf labeled by a string of length at most k, and a binary string alignment function ⊗, an implied alignment can be generated to describe the alignment of a dynamic homology for [Formula: see text]. This is done by first decorating each node of [Formula: see text] with an alignment context using ⊗, in a post-order traversal, then, during a subsequent pre-order traversal, inferring on which edges insertion and deletion events occurred using those internal node decorations.
Results: Previous descriptions of the implied alignment algorithm suggest a technique of "back-propagation" with time complexity [Formula: see text]. Here we describe an implied alignment algorithm with complexity [Formula: see text]. For well-behaved data, such as molecular sequences, the runtime approaches the best-case complexity of Ω(k∗n).
Conclusions: The reduction in the time complexity of the algorithm dramatically improves both its utility in generating multiple sequence alignments and its heuristic utility.
Keywords: Dynamic homology; Implied alignment; Multiple string alignment; Phylogenetics; Sequence alignment; Tree alignment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wheeler WC. Implied alignment. Cladistics. 2003a; 19:261–8. - PubMed
-
- Wheeler WC. Optimization alignment: The end of multiple sequence alignment in phylogenetics? Cladistics. 1996;12:1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1096-0031.1996.tb00189.x. - DOI
-
- Wheeler WC, Gladstein DS. MALIGN. Unknown Month 1991. program and documentation available at http://research.amnh.org/scicomp/projects/malign.php. documentation by Daniel Janies and W. C. Wheeler.
-
- Gladstein DS, Wheeler WC. POY version 2.0.New York: American Museum of Natural History; 1997. http://research.amnh.org/scicomp/projects/poy.php.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources