Patterns, management, and outcomes of traumatic pelvic fracture: insights from a multicenter study
- PMID: 32646448
- PMCID: PMC7344030
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-020-01772-w
Patterns, management, and outcomes of traumatic pelvic fracture: insights from a multicenter study
Abstract
Background: Traumatic pelvic fracture (TPF) is a significant injury that results from high energy impact and has a high morbidity and mortality.
Purpose: We aimed to describe the epidemiology, incidence, patterns, management, and outcomes of TPF in multinational level 1 trauma centers.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of all patients with TPF between 2010 and 2016 at two trauma centers in Qatar and Germany.
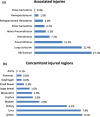
Results: A total of 2112 patients presented with traumatic pelvic injuries, of which 1814 (85.9%) sustained TPF, males dominated (76.5%) with a mean age of 41 ± 21 years. In unstable pelvic fracture, the frequent mechanism of injury was motor vehicle crash (41%) followed by falls (35%) and pedestrian hit by vehicle (24%). Apart from both extremities, the chest (37.3%) was the most commonly associated injured region. The mean injury severity score (ISS) of 16.5 ± 13.3. Hemodynamic instability was observed in 44%. Blood transfusion was needed in one third while massive transfusion and intensive care admission were required in a tenth and a quarter of cases, respectively. Tile classification was possible in 1228 patients (type A in 60%, B in 30%, and C in 10%). Patients with type C fractures had higher rates of associated injuries, higher ISS, greater pelvis abbreviated injury score (AIS), massive transfusion protocol activation, prolonged hospital stay, complications, and mortality (p value < 0.001). Two-thirds of patients were managed conservatively while a third needed surgical fixation. The median length of hospital and intensive care stays were 15 and 5 days, respectively. The overall mortality rate was 4.7% (86 patients).
Conclusion: TPF is a common injury among polytrauma patients. It needs a careful, systematic management approach to address the associated complexities and the polytrauma nature.
Keywords: Hemodynamic instability; Mortality; Pelvic fracture; Tiles’s classification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Demetriades D, Karaiskakis M, Velmahos GC, et al. Pelvic fractures in pediatric and adult trauma patients: are they different injuries? J Trauma. 2003;54:1146–1151. - PubMed
-
- Court-Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury. 2006;37:691–697. - PubMed
-
- Balogh Z, King KL, Mackay P, et al. The epidemiology of pelvic ring fractures: a population-based study. J Trauma. 2007;63:1066–1073. - PubMed
-
- Verbeek DO, Burgess AR. Importance of pelvic radiography for initial trauma assessment: an orthopedic perspective. J Emerg Med. 2016;50(6):852–858. - PubMed
-
- Rommens PM, Wagner D, Hofmann A. Minimal invasive surgical treatment of fragility fractures of the pelvis. Chirurgia (Bucur) 2017;112(5):524–5376. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical