Global Issues of Radiopharmaceutical Access and Availability: A Nuclear Medicine Global Initiative Project
- PMID: 32646881
- PMCID: PMC8049350
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.120.247197
Global Issues of Radiopharmaceutical Access and Availability: A Nuclear Medicine Global Initiative Project
Abstract
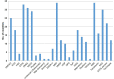
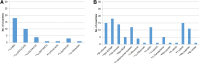
The Nuclear Medicine Global Initiative was formed in 2012 by 13 international organizations to promote human health by advancing the field of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging by supporting the practice and application of nuclear medicine. The first project focused on standardization of administered activities in pediatric nuclear medicine and resulted in 2 articles. For its second project the Nuclear Medicine Global Initiative chose to explore issues impacting on access and availability of radiopharmaceuticals around the world. Methods: Information was obtained by survey responses from 35 countries on available radioisotopes, radiopharmaceuticals, and kits for diagnostic and therapeutic use. Issues impacting on access and availability of radiopharmaceuticals in individual countries were also identified. Results: Detailed information on radiopharmaceuticals used in each country, and sources of supply, was evaluated. Responses highlighted problems in access, particularly due to the reliance on a sole provider, regulatory issues, and reimbursement, as well as issues of facilities and workforce, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Conclusion: Strategies to address access and availability of radiopharmaceuticals are outlined, to enable timely and equitable patient access to nuclear medicine procedures worldwide. In the face of disruptions to global supply chains by the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak, renewed focus on ensuring a reliable supply of radiopharmaceuticals is a major priority for nuclear medicine practice globally.
Keywords: access; global issues; radiopharmaceuticals.
© 2021 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures


References
-
- The supply of medical isotopes: an economic diagnosis and possible solutions. OECD iLibrary website. 10.1787/9b326195-en. Published November 18, 2019. Accessed October 28, 2020. - DOI
-
- National Research Council and Institute of Medicine of the National Academies. Nuclear medicine imaging in diagnosis and treatment. In: Advancing Nuclear Medicine Through Innovation. National Academies Press; 2007:43–58.
-
- Cutler CS. Economics of new molecular targeted personalized radiopharmaceuticals. Semin Nucl Med. 2019;49:450–457. - PubMed
-
- IMAGINE: IAEA Medical imAGIng and Nuclear mEdicine global resources database. IAEA website. https://humanhealth.iaea.org/HHW/DBStatistics/IMAGINE.html. Accessed October 28, 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
