A homozygous missense variant in UBE2T is associated with a mild Fanconi anemia phenotype
- PMID: 32646888
- PMCID: PMC8018101
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2020.259275
A homozygous missense variant in UBE2T is associated with a mild Fanconi anemia phenotype
Figures
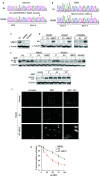
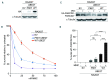

References
-
- Meetei AR, de Winter JP, Medhurst AL, et al. . A novel ubiquitin ligase is deficient in Fanconi anemia. Nat Genet. 2003;35(2):165-170. - PubMed
-
- Machida YJ, Machida Y, Chen Y, et al. . UBE2T is the E2 in the Fanconi anemia pathway and undergoes negative autoregulation. Mol Cell. 2006;23(4):589-596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

