Novel Zinc / Tungsten Carbide Nanocomposite as Bioabsorbable Implant
- PMID: 32647402
- PMCID: PMC7346885
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2019.127282
Novel Zinc / Tungsten Carbide Nanocomposite as Bioabsorbable Implant
Abstract
There is a lack of bioabsorbable materials with adequate mechanical strength suitable for implant applications that provide temporary support while tissue integrity is restored, especially for pediatric applications. Bioabsorbable metals have emerged as an attractive choice due to their combination of strength, ductility, and biocompatibility in vivo. Zinc has shown great promise as a bioabsorbable metal, but the weak mechanical properties of pure zinc limit its application as an implant material. This study investigates zinc-tungsten carbide (Zn-WC) nanocomposite as a novel material for bioabsorbable metallic implants. Ultrasound-assisted powder compaction was used to fabricate Zn-WC nanocomposites. This study includes the material characterization of microstructure, microhardness, and degradability. Results showed that tungsten carbide nanoparticles enhanced the mechanical properties of Zn, and maintained the favorable corrosion rate of pure Zn. These results encourage further investigation of Zn-WC nanocomposites for biomedical applications with the ultimate goal of creating safe and efficacious bioabsorbable metallic implants for many clinical applications.
Keywords: Bioabsorbable implant; Nanocomposites; Zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest Statement All authors in the author list declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
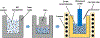
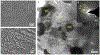
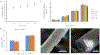
References
-
- Moriarty TF, Schlegel U, Perren S, Richards RG, Infection in fracture fixation: can we influence infection rates through implant design?, Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 21(3) (2010) 1031–1035. - PubMed
-
- Nakata T, Fujii K, Fukunaga M, Shibuya M, Kawai K, Kawasaki D, Naito Y, Ohyanagi M, Masuyama T, Morphological, Functional, and Biological Vascular Healing Response 6 Months After Drug- Eluting Stent Implantation: A Randomized Comparison of Three Drug-Eluting Stents, Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 88(3) (2016) 350–357. - PubMed
-
- Kim MS, Dean LS, In-stent restenosis, Cardiovascular therapeutics 29(3) (2011) 190–198. - PubMed
-
- Sumitomo N, Noritake K, Flattori T, Morikawa K, Niwa S, Sato K, Niinomi M, Experiment study on fracture fixation with low rigidity titanium alloy, Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine (4)(2008)1581–1586. - PubMed
