Cumulative incidence and diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in New York
- PMID: 32648546
- PMCID: PMC7297691
- DOI: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2020.06.004
Cumulative incidence and diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in New York
Abstract
Purpose: New York State (NYS) is an epicenter of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in the United States. Reliable estimates of cumulative incidence in the population are critical to tracking the extent of transmission and informing policies.
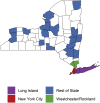
Methods: We conducted a statewide seroprevalence study in a 15,101 patron convenience sample at 99 grocery stores in 26 counties throughout NYS. SARS-CoV-2 cumulative incidence was estimated from antibody reactivity by first poststratification weighting and then adjusting by antibody test characteristics. The percent diagnosed was estimated by dividing the number of diagnoses by the number of estimated infection-experienced adults.
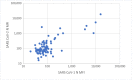
Results: Based on 1887 of 15,101 (12.5%) reactive results, estimated cumulative incidence through March 29 was 14.0% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 13.3%-14.7%), corresponding to 2,139,300 (95% CI: 2,035,800-2,242,800) infection-experienced adults. Cumulative incidence was highest in New York City 22.7% (95% CI: 21.5%-24.0%) and higher among Hispanic/Latino (29.2%), non-Hispanic black/African American (20.2%), and non-Hispanic Asian (12.4%) than non-Hispanic white adults (8.1%, P < .0001). An estimated 8.9% (95% CI: 8.4%-9.3%) of infections in NYS were diagnosed, with diagnosis highest among adults aged 55 years or older (11.3%, 95% CI: 10.4%-12.2%).
Conclusions: From the largest U.S. serosurvey to date, we estimated >2 million adult New York residents were infected through late March, with substantial disparities, although cumulative incidence remained less than herd immunity thresholds. Monitoring, testing, and contact tracing remain essential public health strategies.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Epidemics; Epidemiology; Infectious diseases; Seroepidemiologic studies; Seroprevalence; Surveillance.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- JHU COVID-19 United States Cases 2020. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/us-map
-
- Health NYSDo NYSDOH COVID-19 Tracker 2020. https://covid19tracker.health.ny.gov/views/NYS-COVID19-Tracker/NYSDOHCOV...
-
- Amid Ongoing COVID-19 Pandemic . 2020. Governor Cuomo outlines blueprint to Un-PAUSE New York [press release]https://www.governor.ny.gov/news/amid-ongoing-covid-19-pandemic-governor...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

