Microembolic Signals Detected by Transcranial Doppler Predict Future Stroke and Poor Outcomes
- PMID: 32648610
- PMCID: PMC7721963
- DOI: 10.1111/jon.12749
Microembolic Signals Detected by Transcranial Doppler Predict Future Stroke and Poor Outcomes
Abstract
Background and purpose: Although transcranial Doppler detects microembolic signals (MES) in numerous settings, the practical significance of such findings remains unclear.
Methods: Clinical information from ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack patients (n = 248) who underwent embolic monitoring from January 2015 to December 2018 was obtained.
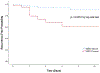
Results: MES were found in 15% of studies and ischemic recurrence was seen in 11% of patients (over 7 ± 6 days). Patients with MES had more lacunes than those without MES (1 ± 3 vs. 1 ± 2, P = .016), were more likely to have ischemic recurrence (37% vs. 6%, P < .001), undergo a future revascularization procedure (26% vs. 10%, P = .005), have a longer length of stay (9 vs. 4 days, P = .043), and have worse functional disability at discharge (modified Rankin Scale 3-6, 66% vs. 34%, P < .001). After controlling for several relevant cofactors, patients with MES were more likely to have ischemic recurrence (HR 4.90, 95% CI 2.16-11.09, P < .001), worse functional disability (OR 3.31, 95% CI 1.22-8.99, P = .019), and longer length of stays (β = .202, P < .001).
Conclusions: MES may help to risk stratify patients as their presence is associated with ischemic recurrence and worse outcomes.
Keywords: Neurosonology; cerebral emboli; recurrence; stroke; transcranial Doppler sonography.
© 2020 American Society of Neuroimaging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microembolic signal detection in acute ischemic stroke: Clinical relevance and impact on treatment individualization-A narrative review.Eur J Neurol. 2025 Jan;32(1):e16584. doi: 10.1111/ene.16584. Eur J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39706201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebral Microembolization in Left Ventricular Assist Device Associated Ischemic Events.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020 Apr;29(4):104660. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104660. Epub 2020 Feb 7. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32044219
-
Countable and non-countable microembolic signals by TCD in first-ever stroke or TIA patients with PFO.J Neurol Sci. 2008 May 15;268(1-2):83-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2007.11.007. Epub 2008 Feb 20. J Neurol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18076907
-
Association of Transcranial Doppler Microembolic Signal With Short-Term Mortality in Acute Ischemic Stroke and Active Cancer.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Aug 6;13(15):e033634. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.033634. Epub 2024 Jul 31. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39082410 Free PMC article.
-
[Detection of micro-embolic signals: a review of the literature].J Mal Vasc. 2012 Dec;37(6):311-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jmv.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Nov 10. J Mal Vasc. 2012. PMID: 23146344 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Infarction Patterns and Recurrent Adverse Cerebrovascular Events in Moyamoya Disease.Dis Markers. 2022 Mar 29;2022:8255018. doi: 10.1155/2022/8255018. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35392499 Free PMC article.
-
Application of transcranial Doppler in cerebrovascular diseases.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Nov 8;14:1035086. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1035086. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36425321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microembolic signal detection in acute ischemic stroke: Clinical relevance and impact on treatment individualization-A narrative review.Eur J Neurol. 2025 Jan;32(1):e16584. doi: 10.1111/ene.16584. Eur J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39706201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perfusion deficit and vessel wall characteristics to predict recurrent ischemic events in medically treated patients with chronic symptomatic anterior circulation large vessel occlusion.Interv Neuroradiol. 2024 Sep 8:15910199241270653. doi: 10.1177/15910199241270653. Online ahead of print. Interv Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 39246035 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors and Clinical Significance of Ultra-Long-Term Microischemia After Intracranial Aneurysm Embolization.Neurol Ther. 2024 Aug;13(4):1173-1190. doi: 10.1007/s40120-024-00630-9. Epub 2024 May 30. Neurol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38814531 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King A, Markus HS. Doppler embolic signals in cerebrovascular disease and prediction of stroke risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 2009;40(12):3711–7. - PubMed
-
- Markus HS, MacKinnon A. Asymptomatic embolization detected by Doppler ultrasound predicts stroke risk in symptomatic carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 2005;36(5):971–5. - PubMed
-
- Babikian VL, Rosales R, Pochay V. Composition of particles associated with embolic signals on transcranial doppler untrasonography. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 1994;4(2):86–90. - PubMed
-
- Gao S, Ka SW, Hansberg T, Lam WWM, Droste DW, Ringelstein EB. Microembolic signal predicts recurrent cerebral ischemic events in acute stroke patients with middle cerebral artery stenosis. Stroke 2004;35(12):2832–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

