Microembolic Signals Detected by Transcranial Doppler Predict Future Stroke and Poor Outcomes
- PMID: 32648610
- PMCID: PMC7721963
- DOI: 10.1111/jon.12749
Microembolic Signals Detected by Transcranial Doppler Predict Future Stroke and Poor Outcomes
Abstract
Background and purpose: Although transcranial Doppler detects microembolic signals (MES) in numerous settings, the practical significance of such findings remains unclear.
Methods: Clinical information from ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack patients (n = 248) who underwent embolic monitoring from January 2015 to December 2018 was obtained.
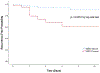
Results: MES were found in 15% of studies and ischemic recurrence was seen in 11% of patients (over 7 ± 6 days). Patients with MES had more lacunes than those without MES (1 ± 3 vs. 1 ± 2, P = .016), were more likely to have ischemic recurrence (37% vs. 6%, P < .001), undergo a future revascularization procedure (26% vs. 10%, P = .005), have a longer length of stay (9 vs. 4 days, P = .043), and have worse functional disability at discharge (modified Rankin Scale 3-6, 66% vs. 34%, P < .001). After controlling for several relevant cofactors, patients with MES were more likely to have ischemic recurrence (HR 4.90, 95% CI 2.16-11.09, P < .001), worse functional disability (OR 3.31, 95% CI 1.22-8.99, P = .019), and longer length of stays (β = .202, P < .001).
Conclusions: MES may help to risk stratify patients as their presence is associated with ischemic recurrence and worse outcomes.
Keywords: Neurosonology; cerebral emboli; recurrence; stroke; transcranial Doppler sonography.
© 2020 American Society of Neuroimaging.
Figures
References
-
- King A, Markus HS. Doppler embolic signals in cerebrovascular disease and prediction of stroke risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 2009;40(12):3711–7. - PubMed
-
- Markus HS, MacKinnon A. Asymptomatic embolization detected by Doppler ultrasound predicts stroke risk in symptomatic carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 2005;36(5):971–5. - PubMed
-
- Babikian VL, Rosales R, Pochay V. Composition of particles associated with embolic signals on transcranial doppler untrasonography. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 1994;4(2):86–90. - PubMed
-
- Gao S, Ka SW, Hansberg T, Lam WWM, Droste DW, Ringelstein EB. Microembolic signal predicts recurrent cerebral ischemic events in acute stroke patients with middle cerebral artery stenosis. Stroke 2004;35(12):2832–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

