Multimarker approach including CRP, sST2 and GDF-15 for prognostic stratification in stable heart failure
- PMID: 32649062
- PMCID: PMC7524044
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12680
Multimarker approach including CRP, sST2 and GDF-15 for prognostic stratification in stable heart failure
Abstract
Aims: Inflammation and cardiac remodelling are common and synergistic pathways in heart failure (HF). Emerging biomarkers such as soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2 (sST2) and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15), which are linked to inflammation and fibrosis process, have been proposed as prognosis factors. However, their potential additive values remain poorly investigated.
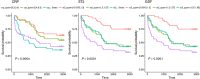
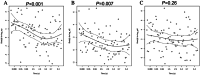
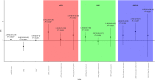
Methods and results: Here, we aimed at evaluating inflammatory and remodelling biomarkers to predict both short-term and long-term mortality in a population with chronic HF in comparison with other classical clinical or biological markers (i.e. N terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide, hs-cTnT, C-reactive protein) alone or using meta-analysis global group in chronic HF risk score in a cohort of 182 patients followed during 80 months (interquartile range: 12.3-90.0). Proportional hazard assumption does not hold for sST2 and C-reactive protein, and follow-up was split into short term (less than 1 year), midterm (between 1 and 5 years), and long term (after 5 years). In univariate analysis, C-reactive protein and sST2 were predictive of short-term mortality but not of middle term and long term whereas GDF-15 was predictive of short and mid-term but not of long-term mortality. In a multivariate model after adjustment for meta-analysis global group in chronic HF score including the three markers, only sST2 was predictive of short-term mortality (P = 0.0225), and only GDF-15 was predictive of middle term mortality (P = 0.0375). None of the markers was predictive of long-term mortality.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that both sST2 and GDF-15 significantly improve the prognosis evaluation of HF patients and suggest that the value of GDF-15 is more sustained overtime and could predict middle term events.
Keywords: Biomarkers; C-reactive protein; GDF-15; Heart failure; Hs-troponin; NT-proBNP; Prognosis; sST2.
© 2020 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002; 420: 868–874. - PubMed
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002; 105: 1135–1143. - PubMed
-
- Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group , Jonathan Emberson null, Derrick Bennett null, Emma Link null, Sarah Parish null, John Danesh null, Jane Armitage null, Rory Collins null . C‐reactive protein concentration and the vascular benefits of statin therapy: an analysis of 20,536 patients in the Heart Protection Study. Lancet Lond Engl 2011; 377: 469–476. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van Tassell BW, Abouzaki NA, Oddi Erdle C, Carbone S, Trankle CR, Melchior RD, Turlington JS, Thurber CJ, Christopher S, Dixon DL, Fronk DT, Thomas CS, Rose SW, Buckley LF, Dinarello CA, Biondi‐Zoccai G, Abbate A. Interleukin‐1 blockade in acute decompensated heart failure: a randomized, double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled pilot study. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2016; 67: 544–551. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

