In Vitro Production of Calcified Bone Matrix onto Wool Keratin Scaffolds via Osteogenic Factors and Electromagnetic Stimulus
- PMID: 32650489
- PMCID: PMC7411850
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13143052
In Vitro Production of Calcified Bone Matrix onto Wool Keratin Scaffolds via Osteogenic Factors and Electromagnetic Stimulus
Abstract
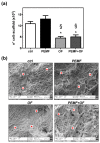
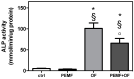
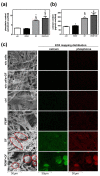
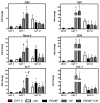
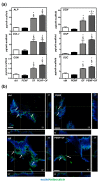
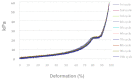
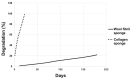
Pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) has drawn attention as a potential tool to improve the ability of bone biomaterials to integrate into the surrounding tissue. We investigated the effects of PEMF (frequency, 75 Hz; magnetic induction amplitude, 2 mT; pulse duration, 1.3 ms) on human osteoblast-like cells (SAOS-2) seeded onto wool keratin scaffolds in terms of proliferation, differentiation, and production of the calcified bone extracellular matrix. The wool keratin scaffold offered a 3D porous architecture for cell guesting and nutrient diffusion, suggesting its possible use as a filler to repair bone defects. Here, the combined approach of applying a daily PEMF exposure with additional osteogenic factors stimulated the cells to increase both the deposition of bone-related proteins and calcified matrix onto the wool keratin scaffolds. Also, the presence of SAOS-2 cells, or PEMF, or osteogenic factors did not influence the compression behavior or the resilience of keratin scaffolds in wet conditions. Besides, ageing tests revealed that wool keratin scaffolds were very stable and showed a lower degradation rate compared to commercial collagen sponges. It is for these reasons that this tissue engineering strategy, which improves the osteointegration properties of the wool keratin scaffold, may have a promising application for long term support of bone formation in vivo.
Keywords: bone tissue engineering; osteogenic factors; pulsed electromagnetic field; wool keratin scaffolds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Osteogenic differentiation potential of mesenchymal stem cells cultured on nanofibrous scaffold improved in the presence of pulsed electromagnetic field.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Feb;233(2):1061-1070. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25962. Epub 2017 Jun 6. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28419435
-
Wool fibril sponges with perspective biomedical applications.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016 Apr 1;61:42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.11.073. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016. PMID: 26838822
-
A comparative analysis of the in vitro effects of pulsed electromagnetic field treatment on osteogenic differentiation of two different mesenchymal cell lineages.Biores Open Access. 2013 Aug;2(4):283-94. doi: 10.1089/biores.2013.0016. Biores Open Access. 2013. PMID: 23914335 Free PMC article.
-
Wool Keratin Nanofibers for Bioinspired and Sustainable Use in Biomedical Field.J Funct Biomater. 2022 Dec 21;14(1):5. doi: 10.3390/jfb14010005. J Funct Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36662052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extraction and application of keratin from natural resources: a review.3 Biotech. 2021 May;11(5):220. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-02734-7. Epub 2021 Apr 16. 3 Biotech. 2021. PMID: 33968565 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing electromagnetic fields to assist bone tissue engineering.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Jan 11;14(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03217-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 36631880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keratose Self-Cross-Linked Wound Dressing for Iron Sequestration in Chronic Wounds.ACS Omega. 2023 Aug 8;8(33):30118-30128. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02525. eCollection 2023 Aug 22. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37636950 Free PMC article.
-
Is Silver Addition to Scaffolds Based on Polycaprolactone Blended with Calcium Phosphates Able to Inhibit Candida albicans and Candida auris Adhesion and Biofilm Formation?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 28;25(5):2784. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052784. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474027 Free PMC article.
-
Human Ovarian Follicular Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells Express Osteogenic Markers When Cultured on Bioglass 58S-Coated Titanium Scaffolds.Materials (Basel). 2023 May 11;16(10):3676. doi: 10.3390/ma16103676. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37241304 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable bioactive scaffold able to stimulate oral bone regeneration on demand.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2025 Apr 8;36(1):31. doi: 10.1007/s10856-025-06879-2. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2025. PMID: 40198381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McLellan J., Thornhill S.G., Shelton S., Kumar M. Keratin-Based Biofilms, Hydrogels, and Biofibers. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2019. pp. 187–200. Chapter 7 of ‘Keratin as a Protein Biopolymer’.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

