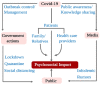
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on socioeconomic and mental health aspects in Nepal
- PMID: 32650687
- PMCID: PMC7443960
- DOI: 10.1177/0020764020942247
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on socioeconomic and mental health aspects in Nepal
Abstract
Background: Public health concern is increasing with recent rise in the number of COVID-19 cases in Nepal. To curb this pandemic, Nepal is facing some forms of lockdown, encouraging people to implement social distancing so as to reduce interactions between people which could eventually reduce the possibilities of new infection; however, it has affected the overall physical, mental, social and spiritual health of the people.
Methods: Published articles related to psychosocial effects due to COVID-19 and other outbreaks were searched and reviewed.
Conclusion: While many countries are supporting their citizens with sophisticated health safety-nets and various relief funds, some developing countries have unique challenges with vulnerable populations and limited resources to respond to the pandemic. This review presents the consequences of pandemic and lockdown on socioeconomic, mental health and other aspects in Nepalese society.
Keywords: COVID-19; mental health; psychosocial; socioeconomic.
Figures
References
-
- Al Jazeera. (2020, April 1). Hundreds of Nepalese stuck at India border amid COVID-19 lockdown. https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2020/04/hundreds-nepalese-stuck-india-bor...
-
- Bhuiyan A. K. M. I., Sakib N., Pakpour A. H., Griffiths M. D., Mamun M. A. (2020). COVID-19-related suicides in Bangladesh due to lockdown and economic factors: Case study evidence from media reports. International Journal of Mental Health Addiction. Advance online publication. 10.1007/s11469-020-00307-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical