Evaluation of MiR-1908-3p as a novel serum biomarker for breast cancer and analysis its oncogenic function and target genes
- PMID: 32650755
- PMCID: PMC7350204
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-07125-4
Evaluation of MiR-1908-3p as a novel serum biomarker for breast cancer and analysis its oncogenic function and target genes
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is one of the most common tumors for women globally. Various miRNAs have been reported to play a crucial role in breast cancer, however the clinical significance of miR-1908-3p in breast cancer remains unclear. The present study aimed to explore the role of miR-1908-3p in breast cancer.
Methods: The expression of miR-1908-3p was detected in 50 pairs of breast cancer tissues and adjacent normal tissues, 60 breast cancer patient serum and 60 healthy volunteer serum. The functional roles of miR-1908-3p in breast cancer cells such as proliferation, migration and invasion were evaluated using CCK8, SRB, wound healing and transwell chambers. In addition, bioinformatics tools were used to identify potential targets of miR-1908-3p.
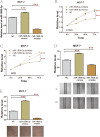
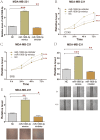
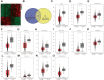
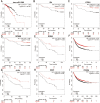
Results: The results showed that the expression of miR-1908-3p were increased in breast cancer tissues and serum compared with normal breast tissues and serum of healthy volunteers respectively. Furthermore, the young breast cancer patients and HER2-positive patients had a higher level of tissues' miR-1908-3p than elder breast cancer patients and HER2-negative patients, respectively. The young breast cancer patients had a higher level of serum miR-1908-3p than elder breast cancer patients, ROC analysis suggested that miR-1908-3p had the potential as a promising serum diagnostic biomarker of breast cancer. Up-regulation of miR-1908-3p promoted the cells proliferation, migration and invasion while knockdown of miR-1908-3p inhibited these processes in breast cancer cell MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. The potential target genes of miR-1908-3p in breast cancer included ID4, LTBP4, GPM6B, RGMA, EFCAB1, ALX4, OSR1 and PPARA. Higher expression of these eight genes correlated with a better prognosis for breast cancer patients.
Conclusions: These results suggest that miR-1908-3p may exert its oncogenic functions via suppression of these eight genes in breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Invasion; Migration; Proliferation; miR-1908-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2016YFE0121900/International S&T Cooperation Program of China
- 2017Y9089/Science and technology innovation joint fund project
- 2019-ZQN-63/Training plan for young and middle-aged key talents
- 2018J01723/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province
- 2019J01278/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

