pssRNAit: A Web Server for Designing Effective and Specific Plant siRNAs with Genome-Wide Off-Target Assessment
- PMID: 32651189
- PMCID: PMC7479913
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.20.00293
pssRNAit: A Web Server for Designing Effective and Specific Plant siRNAs with Genome-Wide Off-Target Assessment
Abstract
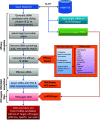
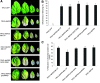
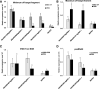
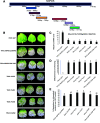
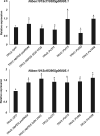
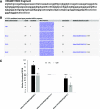
We report an advanced web server, the plant-specific small noncoding RNA interference tool pssRNAit, which can be used to design a pool of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) for highly effective, specific, and nontoxic gene silencing in plants. In developing this tool, we integrated the transcript dataset of plants, several rules governing gene silencing, and a series of computational models of the biological mechanism of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. The designed pool of siRNAs can be used to construct a long double-strand RNA and expressed through virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) or synthetic transacting siRNA vectors for gene silencing. We demonstrated the performance of pssRNAit by designing and expressing the VIGS constructs to silence Phytoene desaturase (PDS) or a ribosomal protein-encoding gene, RPL10 (QM), in Nicotiana benthamiana We analyzed the expression levels of predicted intended-target and off-target genes using reverse transcription quantitative PCR. We further conducted an RNA-sequencing-based transcriptome analysis to assess genome-wide off-target gene silencing triggered by the fragments that were designed by pssRNAit, targeting different homologous regions of the PDS gene. Our analyses confirmed the high accuracy of siRNA constructs designed using pssRNAit The pssRNAit server, freely available at https://plantgrn.noble.org/pssRNAit/, supports the design of highly effective and specific RNAi, VIGS, or synthetic transacting siRNA constructs for high-throughput functional genomics and trait improvement in >160 plant species.
© 2020 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed F, Dai X, Zhao PX(2015) Bioinformatics tools for achieving better gene silencing in plants. Methods Mol Biol 1287: 43–60 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

