Oral or Topical Exposure to Glyphosate in Herbicide Formulation Impacts the Gut Microbiota and Survival Rates of Honey Bees
- PMID: 32651208
- PMCID: PMC7480383
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01150-20
Oral or Topical Exposure to Glyphosate in Herbicide Formulation Impacts the Gut Microbiota and Survival Rates of Honey Bees
Abstract
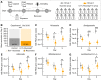
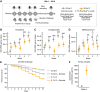
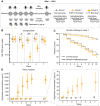
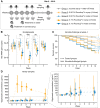
Honey bees are important agricultural pollinators that rely on a specific gut microbiota for the regulation of their immune system and defense against pathogens. Environmental stressors that affect the bee gut microbial community, such as antibiotics and glyphosate, can indirectly compromise bee health. Most of the experiments demonstrating these effects have been done under laboratory conditions with pure chemicals. Here, we investigated the oral and topical effects of various concentrations of glyphosate in a herbicide formulation on the honey bee gut microbiota and health under laboratory and field conditions. Under all of these conditions, the formulation, dissolved in sucrose syrup or water, affected the abundance of beneficial bacteria in the bee gut in a dose-dependent way. Mark-recapture experiments also demonstrated that bees exposed to the formulation were more likely to disappear from the colony, once reintroduced after exposure. Although no visible effects were observed for hives exposed to the formulation in field experiments, challenge trials with the pathogen Serratia marcescens, performed under laboratory conditions, revealed that bees from hives exposed to the formulation exhibited increased mortality compared with bees from control hives. In the field experiments, glyphosate was detected in honey collected from exposed hives, showing that worker bees transfer xenobiotics to the hive, thereby extending exposure and increasing the chances of exposure to recently emerged bees. These findings show that different routes of exposure to glyphosate-based herbicide can affect honey bees and their gut microbiota.IMPORTANCE The honey bee gut microbial community plays a vital role in immune response and defense against opportunistic pathogens. Environmental stressors, such as the herbicide glyphosate, may affect the gut microbiota, with negative consequences for bee health. Glyphosate is usually sprayed in the field mixed with adjuvants, which enhance herbicidal activity. These adjuvants may also enhance undesired effects in nontargeted organisms. This seems to be the case for glyphosate-based herbicide on honey bees. As we show in this study, oral exposure to either pure glyphosate or glyphosate in a commercial herbicide formulation perturbs the gut microbiota of honey bees, and topical exposure to the formulation also has a direct effect on honey bee health, increasing mortality in a dose-dependent way and leaving surviving bees with a perturbed microbiota. Understanding the effects of herbicide formulations on honey bees may help to protect these important agricultural pollinators.
Keywords: Apis mellifera; glyphosate; gut microbiome; herbicide.
Copyright © 2020 Motta et al.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Impact of Glyphosate on the Honey Bee Gut Microbiota: Effects of Intensity, Duration, and Timing of Exposure.mSystems. 2020 Jul 28;5(4):e00268-20. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00268-20. mSystems. 2020. PMID: 32723788 Free PMC article.
-
Glyphosate perturbs the gut microbiota of honey bees.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 9;115(41):10305-10310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803880115. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30249635 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of glyphosate, pure or in herbicide formulation, on bumble bees and their gut microbial communities.Sci Total Environ. 2023 May 10;872:162102. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162102. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 36764553 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial microorganisms for honey bees: problems and progresses.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Nov;100(22):9469-9482. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7870-4. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27717968 Review.
-
Honey bees as models for gut microbiota research.Lab Anim (NY). 2018 Nov;47(11):317-325. doi: 10.1038/s41684-018-0173-x. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Lab Anim (NY). 2018. PMID: 30353179 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbiota composition and gene expression changes induced in the Apis cerana exposed to acetamiprid and difenoconazole at environmentally realistic concentrations alone or combined.Front Physiol. 2023 May 3;14:1174236. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1174236. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37256066 Free PMC article.
-
Glyphosate-Based Herbicides and Their Potential Impact on the Microbiota of Social Bees.Toxics. 2025 Jun 29;13(7):551. doi: 10.3390/toxics13070551. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40710996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insect immunity in the Anthropocene.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2025 Apr;100(2):698-723. doi: 10.1111/brv.13158. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2025. PMID: 39500735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The short neuropeptide F regulates appetitive but not aversive responsiveness in a social insect.iScience. 2021 Dec 11;25(1):103619. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103619. eCollection 2022 Jan 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 35005557 Free PMC article.
-
Testing the Effectiveness of a Commercially Sold Probiotic on Restoring the Gut Microbiota of Honey Bees: a Field Study.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Jun;17(3):991-1000. doi: 10.1007/s12602-023-10203-1. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 38112994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burritt NL, Foss NJ, Neeno-Eckwall EC, Church JO, Hilger AM, Hildebrand JA, Warshauer DM, Perna NT, Burritt JB. 2016. Sepsis and hemocyte loss in honey bees (Apis mellifera) infected with Serratia marcescens strain Sicaria. PLoS One 11:e0167752. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0167752. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

