Immunophenotyping of COVID-19 and influenza highlights the role of type I interferons in development of severe COVID-19
- PMID: 32651212
- PMCID: PMC7402635
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abd1554
Immunophenotyping of COVID-19 and influenza highlights the role of type I interferons in development of severe COVID-19
Abstract
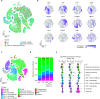
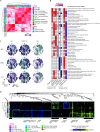
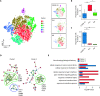
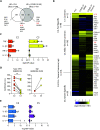
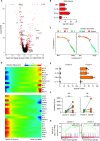
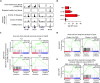
Although most SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals experience mild coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), some patients suffer from severe COVID-19, which is accompanied by acute respiratory distress syndrome and systemic inflammation. To identify factors driving severe progression of COVID-19, we performed single-cell RNA-seq using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) obtained from healthy donors, patients with mild or severe COVID-19, and patients with severe influenza. Patients with COVID-19 exhibited hyper-inflammatory signatures across all types of cells among PBMCs, particularly up-regulation of the TNF/IL-1β-driven inflammatory response as compared to severe influenza. In classical monocytes from patients with severe COVID-19, type I IFN response co-existed with the TNF/IL-1β-driven inflammation, and this was not seen in patients with milder COVID-19. Interestingly, we documented type I IFN-driven inflammatory features in patients with severe influenza as well. Based on this, we propose that the type I IFN response plays a pivotal role in exacerbating inflammation in severe COVID-19.
Copyright © , American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
References
-
- Wu F., Zhao S., Yu B., Chen Y. M., Wang W., Song Z. G., Hu Y., Tao Z. W., Tian J. H., Pei Y. Y., Yuan M. L., Zhang Y. L., Dai F. H., Liu Y., Wang Q. M., Zheng J. J., Xu L., Holmes E. C., Zhang Y. Z., A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 579, 265–269 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W., Li X., Yang B., Song J., Zhao X., Huang B., Shi W., Lu R., Niu P., Zhan F., Ma X., Wang D., Xu W., Wu G., Gao G. F., Tan W.; China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team , A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 727–733 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report –134, June 2, 2020; https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2... (2020).
-
- Guan W. J., Ni Z. Y., Hu Y., Liang W. H., Ou C. Q., He J. X., Liu L., Shan H., Lei C. L., Hui D. S. C., Du B., Li L. J., Zeng G., Yuen K. Y., Chen R. C., Tang C. L., Wang T., Chen P. Y., Xiang J., Li S. Y., Wang J. L., Liang Z. J., Peng Y. X., Wei L., Liu Y., Hu Y. H., Peng P., Wang J. M., Liu J. Y., Chen Z., Li G., Zheng Z. J., Qiu S. Q., Luo J., Ye C. J., Zhu S. Y., Zhong N. S.; China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19 , Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 1708–1720 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

