Functional Connectivity Alterations of the Temporal Lobe and Hippocampus in Semantic Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 32651312
- PMCID: PMC7504988
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-191113
Functional Connectivity Alterations of the Temporal Lobe and Hippocampus in Semantic Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: Semantic memory impairments in semantic dementia are attributed to atrophy and functional disruption of the anterior temporal lobes. In contrast, the posterior medial temporal neurodegeneration found in Alzheimer's disease is associated with episodic memory disturbance. The two dementia subtypes share hippocampal deterioration, despite a relatively spared episodic memory in semantic dementia.
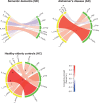
Objective: To unravel mutual and divergent functional alterations in Alzheimer's disease and semantic dementia, we assessed functional connectivity between temporal lobe regions in Alzheimer's disease (n = 16), semantic dementia (n = 23), and healthy controls (n = 17).
Methods: In an exploratory study, we used a functional parcellation of the temporal cortex to extract time series from 66 regions for correlation analysis.
Results: Apart from differing connections between Alzheimer's disease and semantic dementia that yielded reduced functional connectivity, we identified a common pathway between the right anterior temporal lobe and the right orbitofrontal cortex in both dementia subtypes. This disconnectivity might be related to social knowledge deficits as part of semantic memory decline. However, such interpretations are preferably made in a holistic context of disease-specific semantic impairments and functional connectivity changes.
Conclusion: Despite a major limitation owed to unbalanced databases between study groups, this study provides a preliminary picture of the brain's functional disconnectivity in Alzheimer's disease and semantic dementia. Future studies are needed to replicate findings of a common pathway with consistent diagnostic criteria and neuropsychological evaluation, balanced designs, and matched data MRI acquisition procedures.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; functional connectivity; semantic dementia; temporal lobe.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures available online (
Figures


Similar articles
-
The human perirhinal cortex and semantic memory.Eur J Neurosci. 2004 Nov;20(9):2441-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03710.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15525284
-
Preservation of episodic memory in semantic dementia: The importance of regions beyond the medial temporal lobes.Neuropsychologia. 2016 Jan 29;81:50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.12.005. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Neuropsychologia. 2016. PMID: 26683384
-
Common and unique gray matter correlates of episodic memory dysfunction in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's disease.Hum Brain Mapp. 2014 Apr;35(4):1422-35. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22263. Epub 2013 May 14. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014. PMID: 23670951 Free PMC article.
-
Structural magnetic resonance imaging for the early diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease in people with mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 2;3(3):CD009628. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009628.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32119112 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrum of memory dysfunction in degenerative disease.Curr Opin Neurol. 1996 Aug;9(4):281-5. doi: 10.1097/00019052-199608000-00007. Curr Opin Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8858186 Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 related cognitive, structural and functional brain changes among Italian adolescents and young adults: a multimodal longitudinal case-control study.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 2;14(1):402. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-03108-2. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39358346 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-dependent changes in emotional memory associated with cerebral blood flow alterations during Alzheimer's disease progression.Neuroradiology. 2023 Apr;65(4):751-763. doi: 10.1007/s00234-022-03099-1. Epub 2022 Dec 11. Neuroradiology. 2023. PMID: 36502439
-
Proposing a "Brain Health Checkup (BHC)" as a Global Potential "Standard of Care" to Overcome Reward Dysregulation in Primary Care Medicine: Coupling Genetic Risk Testing and Induction of "Dopamine Homeostasis".Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 30;19(9):5480. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095480. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35564876 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial characterization of tangle-bearing neurons and ghost tangles in the human inferior temporal gyrus with three-dimensional imaging.Brain Commun. 2023 Apr 19;5(3):fcad130. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcad130. eCollection 2023. Brain Commun. 2023. PMID: 37324243 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Modal Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease Using Interpretable Graph Convolutional Networks.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2025 Jan;44(1):142-153. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2024.3432531. Epub 2025 Jan 2. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39042528
References
-
- Tulving E (1983) Elements of Episodic Memory, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
-
- Mummery CJ, Patterson K, Price CJ, Ashburner J, Frackowiak RS, Hodges JR (2000) A voxel-based morphometry study of semantic dementia: Relationship between temporal lobe atrophy and semantic memory. Ann Neurol 47, 36–45. - PubMed
-
- McClelland JL, Rogers TT (2003) The parallel distributed processing approach to semantic cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 4, 310–322. - PubMed
-
- Patterson K, Nestor PJ, Rogers TT (2007) Where do you know what you know? The representation of semantic knowledge in the human brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 8, 976–987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

