Analytical sensitivity and efficiency comparisons of SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR primer-probe sets
- PMID: 32651556
- PMCID: PMC9241364
- DOI: 10.1038/s41564-020-0761-6
Analytical sensitivity and efficiency comparisons of SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR primer-probe sets
Abstract
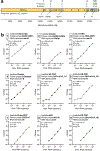
The recent spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) exemplifies the critical need for accurate and rapid diagnostic assays to prompt clinical and public health interventions. Currently, several quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (RT-qPCR) assays are being used by clinical, research and public health laboratories. However, it is currently unclear whether results from different tests are comparable. Our goal was to make independent evaluations of primer-probe sets used in four common SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic assays. From our comparisons of RT-qPCR analytical efficiency and sensitivity, we show that all primer-probe sets can be used to detect SARS-CoV-2 at 500 viral RNA copies per reaction. The exception for this is the RdRp-SARSr (Charité) confirmatory primer-probe set which has low sensitivity, probably due to a mismatch to circulating SARS-CoV-2 in the reverse primer. We did not find evidence for background amplification with pre-COVID-19 samples or recent SARS-CoV-2 evolution decreasing sensitivity. Our recommendation for SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic testing is to select an assay with high sensitivity and that is regionally used, to ease comparability between outcomes.
Figures
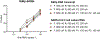
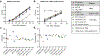

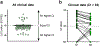
References
-
- Gorbalenya AE et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: The species and its viruses – a statement of the Coronavirus Study Group. bioRxiv 2020.02.07.937862 (2020) doi: 10.1101/2020.02.07.937862. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

