Roles for circulating polyunsaturated fatty acids in ischemic stroke and modifiable factors: a Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 32652993
- PMCID: PMC7354684
- DOI: 10.1186/s12937-020-00582-4
Roles for circulating polyunsaturated fatty acids in ischemic stroke and modifiable factors: a Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background: Available data about the effects of circulating polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) on ischemic stroke (IS) and its main risk factors remains limited and conflicting. Therefore, we conducted Mendelian randomization (MR) to assess whether genetically predicted PUFA affected IS, lipids and blood pressure (BP).
Methods: Genetic instruments associated with IS were derived from ISGC Consortium (n = 29,633), with lipids were derived from GLGC(n = 188,577), with BP were derived from Neale Lab(n = 337,000). The inverse-variance weighted method was the main analysis to estimate the effect of exposure on outcome. Sensitivity analyses included principal components analysis, MR-Egger, weighted median, and weighted mode.
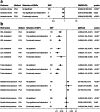
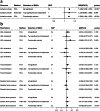
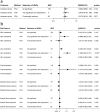
Results: Per SD increases in serum α-linolenic acid (ALA) were associated with lower IS risk, with odd ratio (OR) of 0.867(0.782,0.961), arachidonic acid (AA) were associated with higher IS risk (OR: 1.053(1.014,1.094)). Likewise, Per SD increases in ALA were associated with the lower-level low-density lipoprotein cholesterol(LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), total cholesterol (TC) (β:-0.122(- 0.144, - 0.101), - 0.159(- 0.182, - 0.135), - 0.148(- 0.171, - 0.126), respectively), AA were associated with the higher-level of LDL-C, HDL-C and TC (β:0.045(0.034,0.056), 0.059(0.050,0.067), 0.055(0.046,0.063), respectively). Linoleic acid (LA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) had little or no association with IS, lipids or BP at Bonferroni-corrected significance. Different analytic methods supported these findings. The intercept test of MR-Egger implied no pleiotropy.
Conclusions: High-level plasma ALA was protective for IS but AA was the opposite. LA, EPA, DHA, and DPA had no effects on IS.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Ischemic stroke; Lipids; Mendelian randomization; Omega-3 fatty acids; Omega-6 fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Joseph P, Leong D, McKee M, Anand SS, Schwalm JD, Teo K, et al. Reducing the global burden of cardiovascular disease, part 1: the epidemiology and risk factors. Circ Res. 2017;121:677–694. - PubMed
-
- GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1459–544. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1. - PMC - PubMed
-
- O'Donnell MJ, Chin SL, Rangarajan S, Xavier D, Liu L, Zhang H, et al. Global and regional effects of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with acute stroke in 32 countries (INTERSTROKE): a case-control study. Lancet. 2016; 388: 761–775. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30506-2. - PubMed
-
- Libby P, Buring JE, Badimon L, Hansson GK, Deanfield J, Bittencourt MS, et al. Atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

