The role of DNA methylation in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 32653024
- PMCID: PMC7353744
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-020-00896-4
The role of DNA methylation in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
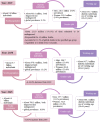
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic condition characterised by β cell dysfunction and persistent hyperglycaemia. The disorder can be due to the absence of adequate pancreatic insulin production or a weak cellular response to insulin signalling. Among the three types of DM, namely, type 1 DM (T1DM), type 2 DM (T2DM), and gestational DM (GDM); T2DM accounts for almost 90% of diabetes cases worldwide.Epigenetic traits are stably heritable phenotypes that result from certain changes that affect gene function without altering the gene sequence. While epigenetic traits are considered reversible modifications, they can be inherited mitotically and meiotically. In addition, epigenetic traits can randomly arise in response to environmental factors or certain genetic mutations or lesions, such as those affecting the enzymes that catalyse the epigenetic modification. In this review, we focus on the role of DNA methylation, a type of epigenetic modification, in the pathogenesis of T2DM.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Diabetes mellitus; Hypermethylation; Hypomethylation; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 8th ed. Brussels; 2017.
-
- Al-Haddad R, Karnib N, Assaad RA, Bilen Y, Emmanuel N, Ghanem A, et al. Epigenetic changes in diabetes. Neurosci Lett. 2016;625:64–69. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 9th ed. Brussels; 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

