Good or bad: Application of RAAS inhibitors in COVID-19 patients with cardiovascular comorbidities
- PMID: 32653530
- PMCID: PMC7346797
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107628
Good or bad: Application of RAAS inhibitors in COVID-19 patients with cardiovascular comorbidities
Abstract
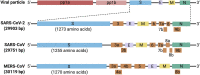
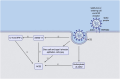
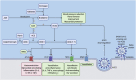
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is caused by a newly emerged coronavirus (CoV) called Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). COVID-19 patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) comorbidities have significantly increased morbidity and mortality. The use of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor type 1 blockers (ARBs) improve CVD outcomes; however, there is concern that they may worsen the prognosis of CVD patients that become infected with SARS-CoV-2 because the virus uses the ACE2 receptor to bind to and subsequently infect host cells. Thus, some health care providers and media sources have questioned the continued use of ACE inhibitors and ARBs. In this brief review, we discuss the effect of ACE inhibitor-induced bradykinin on the cardiovascular system, on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) regulation in COVID-19 patients, and analyze recent clinical studies regarding patients treated with RAAS inhibitors. We propose that the application of RAAS inhibitors for COVID-19 patients with CVDs may be beneficial rather than harmful.
Keywords: Bradykinin; COVID-19; Hypertension; Inflammation; RAAS inhibitors.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Arabi Y.M., Arifi A.A., Balkhy H.H., Najm H., Aldawood A.S., Ghabashi A.…Al Raiy B. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2014;160:389–397. - PubMed
-
- Aztatzi-Aguilar O.G., Uribe-Ramirez M., Arias-Montano J.A., Barbier O., De Vizcaya-Ruiz A. Acute and subchronic exposure to air particulate matter induces expression of angiotensin and bradykinin-related genes in the lungs and heart: Angiotensin-II type-I receptor as a molecular target of particulate matter exposure. Particle and Fibre Toxicology. 2015;12:17. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

