The Genome of the Softshell Clam Mya arenaria and the Evolution of Apoptosis
- PMID: 32653903
- PMCID: PMC7531772
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evaa143
The Genome of the Softshell Clam Mya arenaria and the Evolution of Apoptosis
Abstract
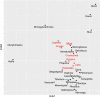
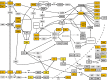
Apoptosis is a fundamental feature of multicellular animals and is best understood in mammals, flies, and nematodes, with the invertebrate models being thought to represent a condition of ancestral simplicity. However, the existence of a leukemia-like cancer in the softshell clam Mya arenaria provides an opportunity to re-evaluate the evolution of the genetic machinery of apoptosis. Here, we report the whole-genome sequence for M. arenaria which we leverage with existing data to test evolutionary hypotheses on the origins of apoptosis in animals. We show that the ancestral bilaterian p53 locus, a master regulator of apoptosis, possessed a complex domain structure, in contrast to that of extant ecdysozoan p53s. Further, ecdysozoan taxa, but not chordates or lophotrochozoans like M. arenaria, show a widespread reduction in apoptosis gene copy number. Finally, phylogenetic exploration of apoptosis gene copy number reveals a striking linkage with p53 domain complexity across species. Our results challenge the current understanding of the evolution of apoptosis and highlight the ancestral complexity of the bilaterian apoptotic tool kit and its subsequent dismantlement during the ecdysozoan radiation.
Keywords: Mya; Ecdysozoa; apoptosis; gene family evolution; softshell clam.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of new microsatellite markers for the invasive softshell clam, Mya arenaria (L.) (Bivalvia: Myidae).Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(2):2515-2520. doi: 10.3390/ijms13022515. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22408468 Free PMC article.
-
Complete mitochondrial genome of the soft-shell clam Mya arenaria.Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal. 2016 Sep;27(5):3553-4. doi: 10.3109/19401736.2015.1074214. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal. 2016. PMID: 26260175 Free PMC article.
-
Biogeography of resistance to paralytic shellfish toxins in softshell clam, Mya arenaria (L.), populations along the Atlantic coast of North America.Aquat Toxicol. 2018 Sep;202:196-206. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.06.017. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Aquat Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30075308
-
p53 Superfamily proteins in marine bivalve cancer and stress biology.Adv Mar Biol. 2011;59:1-36. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385536-7.00001-7. Adv Mar Biol. 2011. PMID: 21724017 Review.
-
Evolution of the animal apoptosis network.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Mar 1;5(3):a008649. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008649. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23457257 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Taxonomic Distribution and Molecular Evolution of Mytilectins.Mar Drugs. 2023 Nov 27;21(12):614. doi: 10.3390/md21120614. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 38132935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phylogenetic analysis of the caspase family in bivalves: implications for programmed cell death, immune response and development.BMC Genomics. 2021 Jan 25;22(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07380-0. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33494703 Free PMC article.
-
The expanded inhibitor of apoptosis gene family in oysters possesses novel domain architectures and may play diverse roles in apoptosis following immune challenge.BMC Genomics. 2022 Mar 12;23(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08233-6. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35279090 Free PMC article.
-
Centuries of genome instability and evolution in soft-shell clam, Mya arenaria, bivalve transmissible neoplasia.Nat Cancer. 2023 Nov;4(11):1561-1574. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00643-7. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Nat Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37783804 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic apoptosis is evolutionarily divergent among metazoans.Evol Lett. 2023 Nov 16;8(2):267-282. doi: 10.1093/evlett/qrad057. eCollection 2024 Apr. Evol Lett. 2023. PMID: 38525035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 215(3):403–410. - PubMed
-
- Andrews S. 2010. FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data [Online]. Available from: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
-
- Anisimova M, Gascuel O. 2006. Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: a fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Syst Biol. 55(4):539–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

