Treatment with rivaroxaban and monitoring of coagulation profiles in two dogs with venous thromboembolism
- PMID: 32655095
- PMCID: PMC7538330
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.19-0605
Treatment with rivaroxaban and monitoring of coagulation profiles in two dogs with venous thromboembolism
Abstract
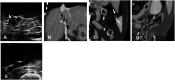
Two dogs with immune-mediated hemolytic anemia complicated with thromboembolism were presented. Both of the dogs were initially treated with immunosuppressive therapy in conjunction with dalteparin and clopidogrel. Although the immunosuppressive therapy was effective, peritoneal effusion due to thromboembolism was observed during the course of the disease in these dogs. After initiation of rivaroxaban treatment, peritoneal effusion decreased immediately in parallel with the normalization of D-dimer, antithrombin (AT), and thrombin-antithrombin complex (TAT). Hematochezia, cutaneous hemorrhage, and hematuria were observed as adverse events after administration of rivaroxaban in one case. Rivaroxaban was effective for the control of thromboembolism secondary to immune-mediated hemolytic anemia, and D-dimer, AT, and TAT were useful to monitor the status of thromboembolic disease in dogs.
Keywords: direct oral anticoagulant; heparin resistance; immune-mediated hemolytic anemia; thrombotic marker; venous thromboembolism.
Figures


References
-
- Beyer-Westendorf J., Förster K., Pannach S., Ebertz F., Gelbricht V., Thieme C., Michalski F., Köhler C., Werth S., Sahin K., Tittl L., Hänsel U., Weiss N.2014. Rates, management, and outcome of rivaroxaban bleeding in daily care: results from the Dresden NOAC registry. Blood 124: 955–962. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-03-563577 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boisclair M. D., Lane D. A., Wilde J. T., Ireland H., Preston F. E., Ofosu F. A.1990. A comparative evaluation of assays for markers of activated coagulation and/or fibrinolysis: thrombin-antithrombin complex, D-dimer and fibrinogen/fibrin fragment E antigen. Br. J. Haematol. 74: 471–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb06337.x - DOI - PubMed

