The Delta-Scoring Method of Tests With Binary Items: A Note on True Score Estimation and Equating
- PMID: 32655171
- PMCID: PMC7328232
- DOI: 10.1177/0013164417724187
The Delta-Scoring Method of Tests With Binary Items: A Note on True Score Estimation and Equating
Abstract
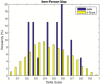
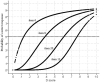
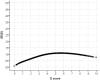
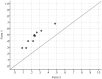
This article presents some new developments in the methodology of an approach to scoring and equating of tests with binary items, referred to as delta scoring (D-scoring), which is under piloting with large-scale assessments at the National Center for Assessment in Saudi Arabia. This presentation builds on a previous work on delta scoring and adds procedures for scaling and equating, item response function, and estimation of true values and standard errors of D scores. Also, unlike the previous work on this topic, where D-scoring involves estimates of item and person parameters in the framework of item response theory, the approach presented here does not require item response theory calibration.
Keywords: assessment; delta-scoring; test equating; test scoring; testing.
© The Author(s) 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Allen J. M., Yen W. M. (1979). Introduction to measurement theory. Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole.
-
- Angoff W. H. (1971). Scales, norms and equivalent scores. In Thorndike R. L. (Ed.), Educational measurement (2nd ed., pp. 508-600). Washington DC: American Council on Education.
-
- Atanasov D. V. (2016. a). A system for automated test assembly (SATA). Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: National Center for Assessment.
-
- Atanasov D. V. (2016. b). A computer program in MATLAB for bootstrap estimation of expected item difficulties on a test of binary items. Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: National Center for Assessment.
-
- Atanasov D. V., Dimitrov D. M. (2015). A system for automated test scoring and equating (SATSE). Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: National Center for Assessment.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
