Understanding the Mechanism of Cell Death in Gemcitabine Resistant Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Systems Biology Approach
- PMID: 32655287
- PMCID: PMC7327974
- DOI: 10.2174/1389202920666191025102726
Understanding the Mechanism of Cell Death in Gemcitabine Resistant Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Systems Biology Approach
Abstract
Background: Gemcitabine is the standard chemotherapeutic drug administered in advanced Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC). However, due to drug resistance in PDAC patients, this treatment has become less effective. Over the years, clinical trials for the quest of finding novel compounds that can be used in combination with gemcitabine have met very little success.
Objective: To predict the driving factors behind pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, and to understand the effect of these components in the progression of the disease and their contribution to cell growth and proliferation.
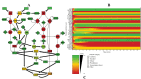
Methods: With the help of systems biology approaches and using gene expression data, which is generally found in abundance, dysregulated elements in key signalling pathways were predicted. Prominent dysregulated elements were integrated into a model to simulate and study the effect of gemcitabine-induced hypoxia.
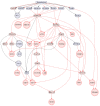
Results: In this study, several transcription factors in the form of key drivers of cancer-related genes were predicted with the help of CARNIVAL, and the effect of gemcitabine-induced hypoxia on the apoptosis pathway was shown to have an effect on the downstream elements of two primary pathway models; EGF/VEGF and TNF signalling pathway.
Conclusion: It was observed that EGF/VEGF signalling pathway played a major role in inducing drug resistance through cell growth, proliferation, and avoiding cell death. Targeting the major upstream components of this pathway could potentially lead to successful treatment.
Keywords: PDAC; apoptosis; cell death; cell signalling; gemcitabine; hypoxia; systems biology.
© 2019 Bentham Science Publishers.
Figures



References
-
- Bray F., Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Siegel R.L., Torre L.A., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. [http://dx.doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492]. [PMID: 30207593]. - PubMed
-
- Aier I., Semwal R., Sharma A., Varadwaj P.K. A systematic assessment of statistics, risk factors, and underlying features involved in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019;58:104–110. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2018.12.001]. [PMID: 30537645]. - PubMed
-
- Adamska A., Domenichini A., Falasca M. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: current and evolving therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017;18(7):E1338. [http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071338]. [PMID: 28640192]. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amrutkar M., Gladhaug I.P. Pancreatic cancer chemoresistance to gemcitabine. Cancers (Basel) 2017;9(11):E157. [http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/cancers9110157]. [PMID: 29144412]. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019;69(1):7–34. [http://dx.doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551]. [PMID: 30620402]. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
