CircRNA hsa_circRNA_0000069 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer through miR-873-5p/TUSC3 axis
- PMID: 32655319
- PMCID: PMC7339483
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-020-01387-5
CircRNA hsa_circRNA_0000069 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer through miR-873-5p/TUSC3 axis
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: circRNA hsa_circRNA_0000069 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer through miR-873-5p/TUSC3 axis.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Jun 13;23(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02964-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37312159 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Cervical cancer (CC) is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in women worldwide, still lacking effective biomarkers and therapies for diagnosis and treatment. CircRNAs are a class of endogenous RNAs that regulate gene expression through interacting with miRNAs, implicating in the progression of cancers. Yet the roles of circRNAs in CC are not fully characterized.
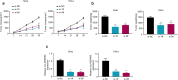
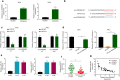
Methods: Fifty pairs of tumor and adjacent normal tissues from CC patients, as well as four CC cell lines and a normal human cervical epithelial cell line were subjected to qRT-PCR assay to assess the mRNA levels of hsa_circ_0000069. CCK-8 and colony formation assays were conducted to detect the proliferation of CC cells. Transwell assay was used to evaluate the migration and invasion capabilities of CC cells. RNA pull-down and luciferase assays were used to determine the interaction between hsa_circ_0000069 and miR-873-5p. A xenograft model of CC was established to verify the in vivo function of hsa_circ_0000069 in CC progression.
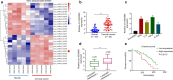
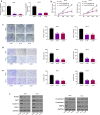
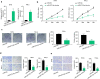
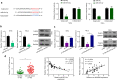
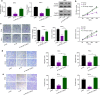
Results: We firstly demonstrated that hsa_circ_0000069 was significantly upregulated and closely related to the lymph node metastasis, and poor prognosis of CC patients. Besides, hsa_circ_0000069 promoted CC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. The knockdown of hsa_circ_0000069 also inhibited CC tumor growth in vivo. Mechanically, we revealed that hsa_circ_0000069 functioned as an oncogene in CC, which is the sponge of miR-873-5p to facilitate the TUSC3 expression, consequently promoting CC progression.
Conclusion: We demonstrated a critical hsa_circ_0000069-miR-873-5p-TUSC3 function network involved in the CC progression, which provides mechanistic insights into the roles of CircRNAs in CC progression and a promising therapeutic target for CC treatment.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; CircRNA; Invasion; Migration; Proliferation; hsa_circ_0000069; miRNA.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hsa_circ_0107593 Suppresses the Progression of Cervical Cancer via Sponging hsa-miR-20a-5p/93-5p/106b-5p.Front Oncol. 2021 Jan 15;10:590627. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.590627. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33585208 Free PMC article.
-
hsa_circ_0008285 Facilitates the Progression of Cervical Cancer by Targeting miR-211-5p/SOX4 Axis.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 May 26;12:3927-3936. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S244317. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32547228 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001829 promotes gastric cancer progression through miR-155-5p/SMAD2 axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 11;39(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01790-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. Retraction in: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Apr 26;42(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02673-6. PMID: 33308284 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Circ_0007534 as new emerging target in cancer: Biological functions and molecular interactions.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 24;12:1031802. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1031802. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36505874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of circ_NRIP1 in tumor development and cancer therapy (Review).Oncol Lett. 2023 Jun 8;26(1):321. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13907. eCollection 2023 Jul. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37332333 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hsa_circ_0000069 Accelerates Cervical Cancer Progression by Sponging miR-1270 to Facilitate CPEB4 Expression.Biochem Genet. 2024 Jun;62(3):1638-1656. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10494-7. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37667097
-
Effect of circPUM1 on radioresistance of cervical cancer cells through targeting miR-144-3p.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Apr 25;51(2):215-224. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2022-0021. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36161300 Free PMC article. English.
-
circ_0001821 Contributes to the Development of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulating MicroRNA-148a-3p/EGFR Axis and Activating Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Mar 17;42(3):e0008921. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00089-21. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35191745 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and circular RNAs and gynecological cancers: focus on metastasis.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 3;13:1215194. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1215194. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37854681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-873-5p: A Potential Molecular Marker for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 5;11:743701. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.743701. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34676171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7–34. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

