Integrated Metabolomic and Lipidomic Analysis Reveals the Neuroprotective Mechanisms of Bushen Tiansui Formula in an A β 1-42-Induced Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 32655770
- PMCID: PMC7322593
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5243453
Integrated Metabolomic and Lipidomic Analysis Reveals the Neuroprotective Mechanisms of Bushen Tiansui Formula in an A β 1-42-Induced Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
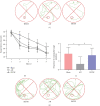
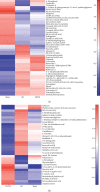
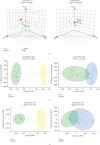
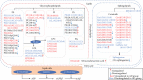
Bushen Tiansui Formula (BSTSF) is a traditional Chinese medicine prescription. It has been widely applied to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD) in the clinic; however, the mechanisms underlying its effects remain largely unknown. In this study, we used a rat AD model to study the effects of BSTSF on cognitive performance, and UPLC-MS/MS-based metabolomic and lipidomic analysis was further performed to identify significantly altered metabolites in the cerebral cortices of AD rats and determine the effects of BSTSF on the metabolomic and lipidomic profiles in the cerebral cortices of these animals. The results revealed that the levels of 47 metabolites and 30 lipids primarily associated with sphingolipid metabolism, glycerophospholipid metabolism, and linoleic acid metabolism were significantly changed in the cerebral cortices of AD rats. Among the altered lipids, ceramides, phosphatidylethanolamines, lysophosphatidylethanolamines, phosphatidylcholines, lysophosphatidylcholines, phosphatidylserines, sphingomyelins, and phosphatidylglycerols showed robust changes. Moreover, 34 differential endogenous metabolites and 21 lipids, of which the levels were mostly improved in the BSTSF treatment group, were identified as potential therapeutic targets of BSTSF against AD. Our results suggest that lipid metabolism is highly dysregulated in the cerebral cortices of AD rats, and BSTSF may exert its neuroprotective mechanisms by restoring metabolic balance, including that of sphingolipid metabolism, glycerophospholipid metabolism, alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism, and D-glutamine and D-glutamate metabolism. Our data may lead to a deeper understanding of the AD-associated metabolic profile and shed new light on the mechanism underlying the therapeutic effects of BSTSF.
Copyright © 2020 Min Yi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no other nonfinancial competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integrated network pharmacology analysis and serum metabolomics to reveal the cognitive improvement effect of Bushen Tiansui formula on Alzheimer's disease.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Mar 1;249:112371. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112371. Epub 2019 Nov 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31683034
-
Untargeted metabolomics analysis of the hippocampus and cerebral cortex identified the neuroprotective mechanisms of Bushen Tiansui formula in an aβ25-35-induced rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 20;13:990307. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.990307. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339577 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of hippocampal transfer RNA-derived small RNAs identifies new potential therapeutic targets of Bushen Tiansui formula against Alzheimer's disease.J Integr Med. 2021 Mar;19(2):135-143. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2020.12.005. Epub 2020 Dec 5. J Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 33334712
-
A metabolomic study based on accurate mass and isotopic fine structures by dual mode combined-FT-ICR-MS to explore the effects of Rhodiola crenulata extract on Alzheimer disease in rats.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019 Mar 20;166:347-356. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.01.021. Epub 2019 Jan 14. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019. PMID: 30690248
-
Enantiomer-specific effects of metamifop on serum metabolism in rats.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Oct 15;285:117008. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.117008. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 39299206 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the Therapeutic Mechanisms of Total Saikosaponins in Alzheimer's Disease: A Metabolomic and Proteomic Approach.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 15;18(1):100. doi: 10.3390/ph18010100. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861162 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology implicates traditional Chinese medicine in regulating systemic homeostasis to benefit Alzheimer's disease.Tzu Chi Med J. 2023 Feb 13;35(2):120-130. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_125_22. eCollection 2023 Apr-Jun. Tzu Chi Med J. 2023. PMID: 37261294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of lipidomics in the study of traditional Chinese medicine.J Pharm Anal. 2025 Feb;15(2):101083. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101083. Epub 2024 Aug 30. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 39995576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics for discovering active ingredients and exploring action mechanism of herbal medicine.Front Chem. 2023 Mar 31;11:1142287. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1142287. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37065828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Analysis of Metabolomics and Lipidomics in Plasma of T2DM Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 8;14(12):2751. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122751. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nichols E., Szoeke C. E. I., Vollset S. E., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet Neurology. 2019;18(1):88–106. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30403-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hou Z., Li F., Chen J., et al. Beneficial Effects of Sagacious Confucius’ Pillow Elixir on Cognitive Function in Senescence-Accelerated P8 Mice (SAMP8) via the NLRP3/Caspase-1 Pathway. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2019;2019:13. doi: 10.1155/2019/3097923.3097923 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

