Influence of major BCR-ABL1 transcript subtype on outcome in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase treated frontline with nilotinib
- PMID: 32655840
- PMCID: PMC7335668
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.27652
Influence of major BCR-ABL1 transcript subtype on outcome in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase treated frontline with nilotinib
Abstract
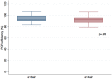
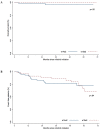
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by the presence of BCR-ABL1 transcript as a result of reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22. The most common transcripts subtypes are e13a2 (b2a2) and e14a2 (b3a2). The prognostic impact of the type of BCR-ABL1 transcript has been the subject of controversies over time. In the imatinib era, several studies have suggested a deeper and faster response in patients expressing e14a2. However, the impact on response after first line therapy with a second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor, nilotinib, is unknown. We retrospectively evaluated 118 patients newly diagnosed with chronic phase CML and treated frontline with nilotinib inside or outside clinical trial in five French centers. Only patients expressing e14a2 or e13a2 transcripts alone were analyzed. At baseline, 55.3% expressed e14a2, 44.7% expressed e13a2. The median age was 51 years and median follow-up was 49 months. Relative risks of CML at diagnosis were similar according to the ELTS score (p = .87). Complete hematological response and complete cytogenetic response rates were similar among groups. Patients expressing e14a2 transcripts compared to e13a2 transcripts had deeper and faster molecular responses, when considering MMR (100% vs 84.1%, p = .007) with a median time of 6.7 and 17.1 months or MR4.5 (100% vs 59.9%, p = .005) with a median time of 39.7 and 70.9 months, respectively. A sustained treatment free remission was observed in 10/10 patients with e14a2 versus 1/3 with e13a2 transcript (p = .04). In conclusion, even treated with nilotinib first line, patients with chronic phase CML expressing BCR-ABL1 e13a2 transcript have a lower rate of deep molecular responses.
Keywords: BCR-ABL1; CML; e13a2; e14a2; nilotinib.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

