Cryptococcal Choroid Plexitis and Non-Communicating Hydrocephalus
- PMID: 32656028
- PMCID: PMC7346368
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.8512
Cryptococcal Choroid Plexitis and Non-Communicating Hydrocephalus
Abstract
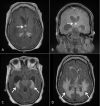
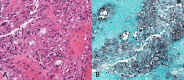
Cryptococcus neoformans is a fungus that commonly invades the central nervous system. While the choroid plexus, the site of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier, serves as one potential entry point for the pathogen, disease involvement of the choroid plexus itself remains a very rare manifestation of Cryptococcus infection. In cases in which choroid plexus involvement blocks cerebrospinal fluid flow, obstructive hydrocephalus may occur. Here we report the case of a 63-year-old woman who presented with choroid plexitis causing obstructive hydrocephalus at the foramen of Monro. Endoscopic biopsy confirmed Cryptococcus neoformans, and the patient was successfully treated with amphotericin, flucytosine, and fluconazole. With proper recognition and treatment of this pathology, patients can fully recover from this condition.
Keywords: biopsy; cryptococcus neoformans; endoscopic; hydrocephalus; infection.
Copyright © 2020, O'Connor et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- MRI features of choroid plexitis. Cho IC, Chang KH, Kim YH, Kim SH, Yu IK, Han MH. Neuroradiology. 1998;40:303–307. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
