The Murmur Online Learning Experience (MOLE) Curriculum Improves Medical Students' Ability to Correctly Identify Cardiac Murmurs
- PMID: 32656325
- PMCID: PMC7331965
- DOI: 10.15766/mep_2374-8265.10904
The Murmur Online Learning Experience (MOLE) Curriculum Improves Medical Students' Ability to Correctly Identify Cardiac Murmurs
Abstract
Introduction: Physical examination skills are receiving less attention in curricula and clinical practice, being supplanted by imaging and other technologies. We developed an online module to introduce auscultation of common cardiac murmurs to second-year medical students.
Methods: The Murmur Online Learning Experience (MOLE) curriculum focused on nine common, unique, or highly testable cardiac murmurs, chosen collaboratively by the authors. The curriculum consisted of (1) a nine-item multiple-choice pretest containing a clinical vignette, a photo of stethoscope location, and an auditory clip; (2) nine modules each containing a several-minute-long auditory clip and a written description (location, quality, radiation, change with exam maneuvers); and (3) a nine-item multiple-choice posttest, identical to the pretest but randomly ordered. All second-year medical students at the University of Louisville were given access to MOLE during their cardiovascular curriculum and given an incentive to complete the ungraded activity.
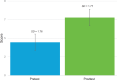
Results: One hundred forty-seven (91.8%) students voluntarily completed the pretest and posttest. The mean pretest score was 3.76 out of 9 (SD = 1.77). The mean posttest score was 7.14 out of 9 (SD = 1.78). Paired t-test results demonstrated a p value of <.001.
Discussion: An online murmur curriculum consisting of repetitive auditory murmurs and narrative description of murmurs improved second-year medical students' ability to correctly identify common cardiac murmurs. This method of learning murmurs via online curriculum is a practical and effective way to hone students' physical exam skills in the modern era.
Keywords: Auscultation; Cardiac; Friction Rub; Heart; Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy; Murmur; Patent Ductus Arteriosis; Regurgitation; Stenosis; Ventricular Septal Defect.
© 2020 Power et al.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources