Esophageal extracellular matrix hydrogel mitigates metaplastic change in a dog model of Barrett's esophagus
- PMID: 32656339
- PMCID: PMC7329334
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba4526
Esophageal extracellular matrix hydrogel mitigates metaplastic change in a dog model of Barrett's esophagus
Abstract
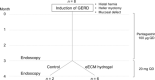
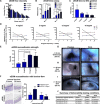
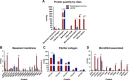
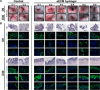
Chronic inflammatory gastric reflux alters the esophageal microenvironment and induces metaplastic transformation of the epithelium, a precancerous condition termed Barrett's esophagus (BE). The microenvironmental niche, which includes the extracellular matrix (ECM), substantially influences cell phenotype. ECM harvested from normal porcine esophageal mucosa (eECM) was formulated as a mucoadhesive hydrogel, and shown to largely retain basement membrane and matrix-cell adhesion proteins. Dogs with BE were treated orally with eECM hydrogel and omeprazole (n = 6) or omeprazole alone (n = 2) for 30 days. eECM treatment resolved esophagitis, reverted metaplasia to a normal, squamous epithelium in four of six animals, and downregulated the pro-inflammatory tumor necrosis factor-α+ cell infiltrate compared to control animals. The metaplastic tissue in control animals (n = 2) did not regress. The results suggest that in vivo alteration of the microenvironment with a site-appropriate, mucoadhesive ECM hydrogel can mitigate the inflammatory and metaplastic response in a dog model of BE.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC BY).
Figures

References
-
- Bissell M. J., Hall H. G., Parry G., How does the extracellular matrix direct gene expression? J. Theor. Biol. 99, 31–68 (1982). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

