Umbilical cord blood-derived ILC1-like cells constitute a novel precursor for mature KIR+NKG2A- NK cells
- PMID: 32657756
- PMCID: PMC7358013
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.55232
Umbilical cord blood-derived ILC1-like cells constitute a novel precursor for mature KIR+NKG2A- NK cells
Abstract
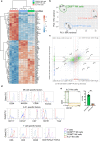
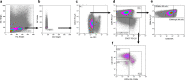
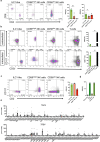
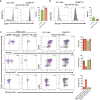
Despite their identification several years ago, molecular identity and developmental relation between human ILC1 and NK cells, comprising group 1 ILCs, is still elusive. To unravel their connection, thorough transcriptional, epigenetic, and functional characterization was performed from umbilical cord blood (CB). Unexpectedly, ILC1-like cells lacked Tbet expression and failed to produce IFNγ. Moreover, in contrast to previously described ILC1 subsets they could be efficiently differentiated into NK cells. These were characterized by highly diversified KIR repertoires including late stage NKG2A-KIR+ effector cells that are commonly not generated from previously known NK cell progenitor sources. This property was dependent on stroma cell-derived Notch ligands. The frequency of the novel ILC1-like NK cell progenitor (NKP) significantly declined in CB from early to late gestational age. The study supports a model in which circulating fetal ILC1-like NKPs travel to secondary lymphoid tissues to initiate the formation of diversified NK cell repertoires after birth.
Keywords: ILC1; Innate lymphoid cells; KIR; NK cells; human; immunology; inflammation; neonatal.
© 2020, Bennstein et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SB, SW, AM, NS, AN, KR, GK, LW, MU No competing interests declared
Figures











References
-
- Adey A, Morrison HG, Asan, Xun X, Kitzman JO, Turner EH, Stackhouse B, MacKenzie AP, Caruccio NC, Zhang X, Shendure J. Rapid, low-input, low-bias construction of shotgun fragment libraries by high-density in vitro transposition. Genome Biology. 2010;11:R119. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-12-r119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernink JH, Peters CP, Munneke M, te Velde AA, Meijer SL, Weijer K, Hreggvidsdottir HS, Heinsbroek SE, Legrand N, Buskens CJ, Bemelman WA, Mjösberg JM, Spits H. Human type 1 innate lymphoid cells accumulate in inflamed mucosal tissues. Nature Immunology. 2013;14:221–229. doi: 10.1038/ni.2534. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cella M, Gamini R, Sécca C, Collins PL, Zhao S, Peng V, Robinette ML, Schettini J, Zaitsev K, Gordon W, Bando JK, Yomogida K, Cortez V, Fronick C, Fulton R, Lin LL, Gilfillan S, Flavell RA, Shan L, Artyomov MN, Bowman M, Oltz EM, Jelinsky SA, Colonna M. Subsets of ILC3-ILC1-like cells generate a diversity spectrum of innate lymphoid cells in human mucosal tissues. Nature Immunology. 2019;20:980–991. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0425-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

