The Inhibitory Effect of Carboplatin Injection on Human Neuroblastoma SK-N-SH
- PMID: 32659114
- PMCID: PMC7586261
- DOI: 10.1177/0963689720920815
The Inhibitory Effect of Carboplatin Injection on Human Neuroblastoma SK-N-SH
Abstract
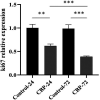
The purpose of our study was to investigate the inhibitory effect of carboplatin injection on human neuroblastoma human neuroblastoma cell (SK-N-SH) cells and to clarify its action mechanism. In this study, human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells were divided into two groups. The treatment group was intervened by carboplatin injection (25 μM), while the control group was intervened by drug solvent. After treating separately for 24 and 72 h, the cells were collected, and western blot (WB) and real-time PCR were used to detect the expression of the proliferation marker protein (Ki67); cells grown on cover slips were prepared and immunocytochemistry (ICC) and hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining were adopted to observe the protein expression of Ki67 and the morphological changes of the cells; clone formation assay was used to detect the clonality of each cell group. The cytotoxicity of carboplatin on SK-N-SH cell was checked by AlamarBlue viability test. Both WB and PCR results showed that after cells were injected with carboplatin for 24 and 72 h, the expression levels of both Ki67 gene and protein were decreased, and they had a significant difference from those of the control group. Carboplatin injection inhibited the expression of Ki67, and the inhibitory effect was particularly significant as the action time prolonged. ICC results showed that the protein expression of Ki67 in the treatment group was lower than that in the control group, and there was a significant difference in expression between them. As shown by HE results, the number of cell necrosis and apoptosis in the treatment group was significantly higher than that in the control group, while the results of clone formation assay showed that in the treatment group, after being injected with carboplatin, the proliferation ability of cells was inhibited, so the number of cells was significantly reduced compared with that of the control group. Carboplatin at the tested concentration displayed no cytotoxicity on SK-N-SH cell. The conclusions are that carboplatin injection can inhibit human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells, and the longer it acts on SK-N-SH cells, the more obvious the inhibitory effect would be.
Keywords: Ki67; carboplatin injection; human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Low dose of arsenic trioxide inhibits multidrug resistant-related P-glycoprotein expression in human neuroblastoma cell line.Int J Oncol. 2016 Dec;49(6):2319-2330. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3756. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27840903
-
[Effects of miR-144 on proliferation, apoptosis and cisplatin resistance by targeting MYCN in pediatric neuroblastoma].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2019 Jul 23;41(7):516-521. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2019.07.006. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31357838 Chinese.
-
Ouabain-Induced Signaling and Cell Survival in SK-N-SH Neuroblastoma Cells Differentiated by Retinoic Acid.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2015;14(10):1343-9. doi: 10.2174/1871527314666150821103008. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 26295826 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of carboplatin injection on Bcl-2 protein expression and apoptosis induction in Raji cells.Eur J Histochem. 2020 Jul 9;64(3):3134. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2020.3134. Eur J Histochem. 2020. PMID: 32643899 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of STAT3-related pathway in SK-N-SH cells by natural product astaxanthin.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Nov 29;23(1):430. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04267-3. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 38031104 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting Oncogenic Transcriptional Networks in Neuroblastoma: From N-Myc to Epigenetic Drugs.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 28;22(23):12883. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312883. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tsubota S, Kadomatsu K. Origin and initiation mechanisms of neuroblastoma. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;372(2):211–221. - PubMed
-
- Nishikawa S, Noguchi H, Tokumitsu T, Ohno A, Moriguchi-Goto S, Maekawa K, Asada Y, Moritake H, Kinoshita M, Yamada A, Takamura K, et al. Diagnosis of pediatric neuroblastoma by urine cytology: a case report. Diagn Cytopathol. 2018;46(3):280–283. - PubMed
-
- Bansal D, Totadri S, Chinnaswamy G, Agarwala S, Vora T, Arora B, Prasad M, Kapoor G, Radhakrishnan V, Laskar S, Kaur T, et al. Management of Neuroblastoma: ICMR Consensus Document. Indian J Pediatr. 2017;84(6):446–455. - PubMed
-
- Kiyonari S, Kadomatsu K. Neuroblastoma models for insights into tumorigenesis and new therapies. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2015;10(1):53–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

