Hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma in South Africa in the era of HIV
- PMID: 32660431
- PMCID: PMC7359588
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-020-01372-2
Hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma in South Africa in the era of HIV
Abstract
Background: Patients co-infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are at risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In sub-Saharan Africa, the overlap between high HIV and HBV prevalence may increase the incidence of HCC. This study investigated the impact of HBV/HIV co-infection on age at presentation and survival of HCC.
Methods: Ethical approval was obtained to recruit, following informed written consent, patients diagnosed with HCC at oncology units at four South African hospitals. Between December 2012 and August 2015, patients newly diagnosed with HCC were recruited and provided demographic and clinical data and blood specimens. Patients were tested for HBV, hepatitis C virus (HCV) and HIV. Survival data was available for a subset of patients.
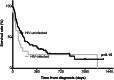
Results: Of 107 HCC cases, 83 (78%) were male. Median age was 46 years (range 18 to 90 years), 68/106 (64%) were HBsAg-positive, and 22/100 (22%) were HIV infected. Among HBV surface antigen (HBsAg)-positive HCC cases, 18/66 (27%) were HIV-infected compared to 3/34 (9%) among those that were HBsAg-negative (p = 0.04). A greater proportion of HBV/HIV co-infected cases were female than HBV mono-infected (6/18, 33% vs 6/47, 13%; p = 0.005). In addition, HBV/HIV co-infected females presented at a younger mean age (36.8 years) than HBV mono-infected women (50.5 years) (p = 0.09). Median survival was 82 days among the HIV-infected HCC patients compared to 181 days among those without HIV (p = 0.15).
Conclusions: HCC is an important complication in the HIV/HBV infected patient. HIV-positive patients presented with HCC at a younger age than HIV-negative patients, this effect appears to be greater in women. These data provide more evidence supporting the call to address. HCC as a cause of morbidity and mortality in the HBV/HIV co-infected patient population. (281 words).
Keywords: Age at presentation; HIV infection; Hepatitis B infection; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Natural history; Survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous