Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19
- PMID: 32660650
- PMCID: PMC7356137
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-020-03120-0
Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19
Abstract
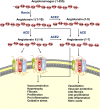
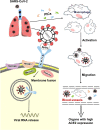
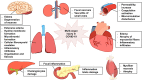
An outbreak of pneumonia caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that started in Wuhan, China, at the end of 2019 has become a global pandemic. Both SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV enter host cells via the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, which is expressed in various human organs. We have reviewed previously published studies on SARS and recent studies on SARS-CoV-2 infection, named coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) by the World Health Organization (WHO), confirming that many other organs besides the lungs are vulnerable to the virus. ACE2 catalyzes angiotensin II conversion to angiotensin-(1-7), and the ACE2/angiotensin-(1-7)/MAS axis counteracts the negative effects of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), which plays important roles in maintaining the physiological and pathophysiological balance of the body. In addition to the direct viral effects and inflammatory and immune factors associated with COVID-19 pathogenesis, ACE2 downregulation and the imbalance between the RAS and ACE2/angiotensin-(1-7)/MAS after infection may also contribute to multiple organ injury in COVID-19. The SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, which binds to ACE2, is a potential target for developing specific drugs, antibodies, and vaccines. Restoring the balance between the RAS and ACE2/angiotensin-(1-7)/MAS may help attenuate organ injuries. SARS-CoV-2 enters lung cells via the ACE2 receptor. The cell-free and macrophage-phagocytosed virus can spread to other organs and infect ACE2-expressing cells at local sites, causing multi-organ injury.
Keywords: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; COVID-19; Multi-organ injury; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, Godbout K, Gosselin M, Stagliano N, et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ Res. 2000;87:E1–E9. - PubMed
-
- Patel S, Rauf A, Khan H, Abu-Izneid T. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAAS): the ubiquitous system for homeostasis and pathologies. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;94:317–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

